HYPERCURVE
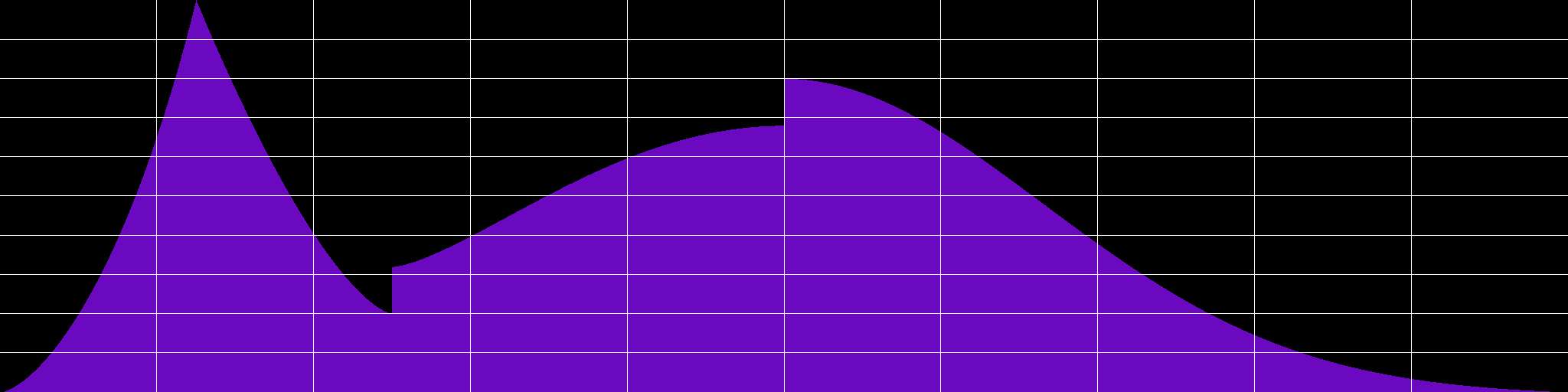 This hypercurve is a combination of 1/8 diocles curve, 1/8 toxoid curve, 2/8 mouth curve, and 4/8 gauss curve.
This hypercurve is a combination of 1/8 diocles curve, 1/8 toxoid curve, 2/8 mouth curve, and 4/8 gauss curve.
What is it ?
Hypercurve is a library allowing you to combine several curve algorithms into a single 2D envelope. It is designed to be used in audio applications, for people who know how to enjoy a finely shaped curve. As shown above, you can perfectly combine gaussian curve with diocles cissoid curve, and plenty of other curve algorithms. The library can be used in C++, Lua, Csound and Faust.
Every curve algorithm is different. In audio applications, we use to assign envelopes to any kind of parameter. In computer music, the way a value goes up and down in time has a big influence on how we hear a sound. Thus, the possibility to create finely shaped envelopes is truly essential. This is the purpose of Hypercurve.
Implemented curve algorithms
-
Cissoid (Diocles curve)
-
Cubic
-
Power curve (choose your power of x)
-
Bezier (Cubic & Quadratic)
-
Cubic Spline - Not implemented in Csound yet
-
Catmull Rom Spline
-
Hanning / Hamming / Blackamn
-
Gauss
-
Toxoid (aka duplicatrix_cubic)
-
Catenary (aka funicular)
-
Tightrope Walker curve
-
Mouth curve
-
Bicorn curve
-
Typed curves : inspired from Csounds GEN16
-
User defined curves - pass it a function (or a lambda in C++), that returns y for any x between 0 and 1. Not implemented in Csound.
## How to install, and make it work
Go to Releases, and download the latest version.
Csound install
To install HYPERCURVES opcodes for Csound, the recommanded way is to move the csound_hypercurve library to the plugins repository of Csound.
Usually, the following instructions will work. If Csound is installed in another location, just change the following path :
- On Windows, move
csound_hypercurve.dlltoC:/Program Files/Csound6_x64/plugins64/. - On MacOS, move
libcsound_hypercurve.dylibto/Library/Frameworks/CsoundLib64.framework/Versions/6.0/Resources/Opcodes64 - On Linux (debian), move
libcsound_hypercurve.soto/usr/local/lib/csound/plugins64/
### Lua use
On every OS Hypercurve is compiled for, you can write a lua script using Hypercurve in the Hypercurve directory and just use it from the terminal with ./luajit myscript.lua. Just change myscript.lua to the name of your script.
On Windows, it should be ̀./luajit.exe myscript.lua.
How to use it
There are three ways to use it : in C++, Csound, Faust or in Lua. Cmake will help you build libraries that can be used in those languages. You will find C++ example under hypercurve_test/test.cpp, Csound example under csound_opcode/test.csd, and Lua example under lua_module/test.lua.
The basic syntax stands as follow :
-
hypercurve(integer size, double y_start, {segment_list});Wheresizeis the size in samples,y_startis the starting point of the curve, and segment list is a list of segments. -
segment(double frac, double y_destination, curve_type crv);Wherefracis the fractional size of the segment (fraction between 0 and 1),y_destinationis the target point, andcrva curve algorithm picked from hypercurve.
A simple C++ example
#include"hypercurve.h"
using namespace hypercurve;
const int definition = 16384;
double y_start = 0;
curve c(definition, y_start,
{
// segment(fractional_size, y_destination, curve
segment(fraction(1,2), 1.0, share(cissoid_curve(1))),
segment(0.5, 0.0, share(blackman_curve()))
});
// Then access samples with double *get_samples()
c.get_samples();A simple Csound example
instr 1
icrv = hc_hypercurve(2048, 0,
hc_segment(1/2, 1, hc_diocles_curve(1)),
hc_segment(1/2, 0, hc_hanning_curve()))
kenv = hc_run(icrv, linseg(0, p3, 1))
ao = vco2(0.3, 300) * kenv
outs(ao, ao)
endinA simple Lua example
package.cpath = package.cpath .. ";/your/path/to/hypercurve/?.so;"
local hc = require("liblua_hypercurve")
local definition = 16384
local y_start = 0
local crv = hc.hypercurve(definition, y_start,
{
hc.segment(1/2, 1.0, hc.cissoid_curve(1.0)),
hc.sement(1/2, 0.0, hc.cubic_curve(0.0))
})
// Write as 24 bits 48KHz wav
hc.write_as_wav("path/to/outfile.wav", crv)A simple Faust example
hc = library("hypercurve.lib");
definition = 16384;
y_start = 0;
curve = hc.hypercurve(definition, y_start (
hc.segment(1/2, 1.0, hc.cissoid_curve(1.0)),
hc.segment(1/2, 0.0, hc.cubic_curve)
));
// Run with interpolation
env = hc.runi(curve, os.phasor(1, 1));Build
First clone the repo with submodules :
git clone https://github.com/johannphilippe/hypercurve.git --recurse-submodules
You should check that Lua is installed on your system. If it is not, or if compilation retrns error, you should install a Lua 5.1 version to the standard installation path. Make sure you have the dynamic library installed, and the headers lauxlib.h and lua.h are available on your system.
Then :
cd hypercurve
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DBUILD_ALL=TRUE
make
If you just want to build for Faust, Lua or Csound, then just use
cmake .. -DBUILD_CSOUND_OPCODE=TRUE
cmake .. -DBUILD_LUA_MODULE=TRUE
cmake .. -DBUILD_FAUST_LIB=TRUE
On some platforms (e.g. Windows) you might need to set the Lua paths with the following options :
cmake .. -DBUILD_LUA_MODULE=TRUE -DLUA_INCLUDE_DIR=/you/dir/include -DLUA_LIBRARIES=/path/to/lua.lib
Windows build for Lua is a bit more complicated, due to the way Windows searches for dynamic libraries. Wheter you provide LUA_LIBRARIES yourself or let CMake find it, you will need the .lib and .dll libraries of Lua to share the same name (except the extension) and the same path (as it is the case in standard Lua distributions). This will allow CMake to copy the Lua .dll dynamic library next to lua_hypercurve in the bin folder.
In order to build the Faust library, you will need Quom to be installed in your system. See the Faust README
The PNG writer fpng used for hypercurve has SSE support. This can be enabled with -DSSE=1.
The resulting binaries will all be located in bin directory. On Windows, lua_hypercurve.dll and hypercurve.dll require sndfile.dll to be in the same folder. lua_hypercurve.dll also requires the Lua .dll you linked against (e.g. lua5.1.dll).
This must be considered when packaging the library to be embedded or used by another application.
TODO
- To fix : Lagrange polynomial returns nan, and doesn't scal well
Ideas :
-
Inversion across the axis of another curve
-
Rename vinvert to reflect the fact it's not vertical symmetry, but linear axis vertical reflection
-
Implement real vertical symmetry
-
Implement that for full curves also
-
Reflect those changes to doc
-
Subdivide segments (only take an upsampled half for example)
-
Interp(0.25) returns an interpolation of two curves (crv1 * 0.25, crv2 * 0.75)
-
extract curve -> subsample from audio, or another method (based on relevant samples)
-
Abs for waveforms
-
Virtual 3D manipulation (rotate z axis)
-
Improve hc_resize to resize curve without creating new one (temp memory)
-
Documentation on hc_resize, and hc_cubic_spline_curve
-
Propagate resize to Lua, Faust and C++ api
-
Gen automatic number : does not take "f" statements into account
-
Waveform scaling : will only work if min_y = max_y : make a specific function
-
Expose random generators to frontends (Lua, Csound, Faust).
-
Tests on invert function (Lua and Csound)
-
REAPER/Reascript -> see https://forum.cockos.com/showthread.php?p=2543755#post2543755
-
Lagrange interpolation for curve extraction ?
-
Hard one -> all curves allowing one sample processing (including cubic spline) to allow no-table processing.
Curves to implement
- Cardioid / hypercardioid
- Elastic curve : https://mathcurve.com/courbes2d.gb/linteaire/linteaire.shtml
- Simple log/exp ?
- Kulp quartic
- Puntiforme https://mathcurve.com/courbes2d/puntiforme/puntiforme.shtml
- Legendre polynome
- Ideas here https://mathcurve.com/courbes2d/courbes2d.shtml
External libraries
The project uses LuaJIT as a submodule, allowing you to try HYPERCURVE out of the box.
It also includes source files from several open-source projects :
- AsciiPlot source code with license under src/asciiplot folder.
- lua-compat-5.3 which provides an API compatibility from 5.1 to 5.3
- fpng - a great C++ PNG reader/writer.``