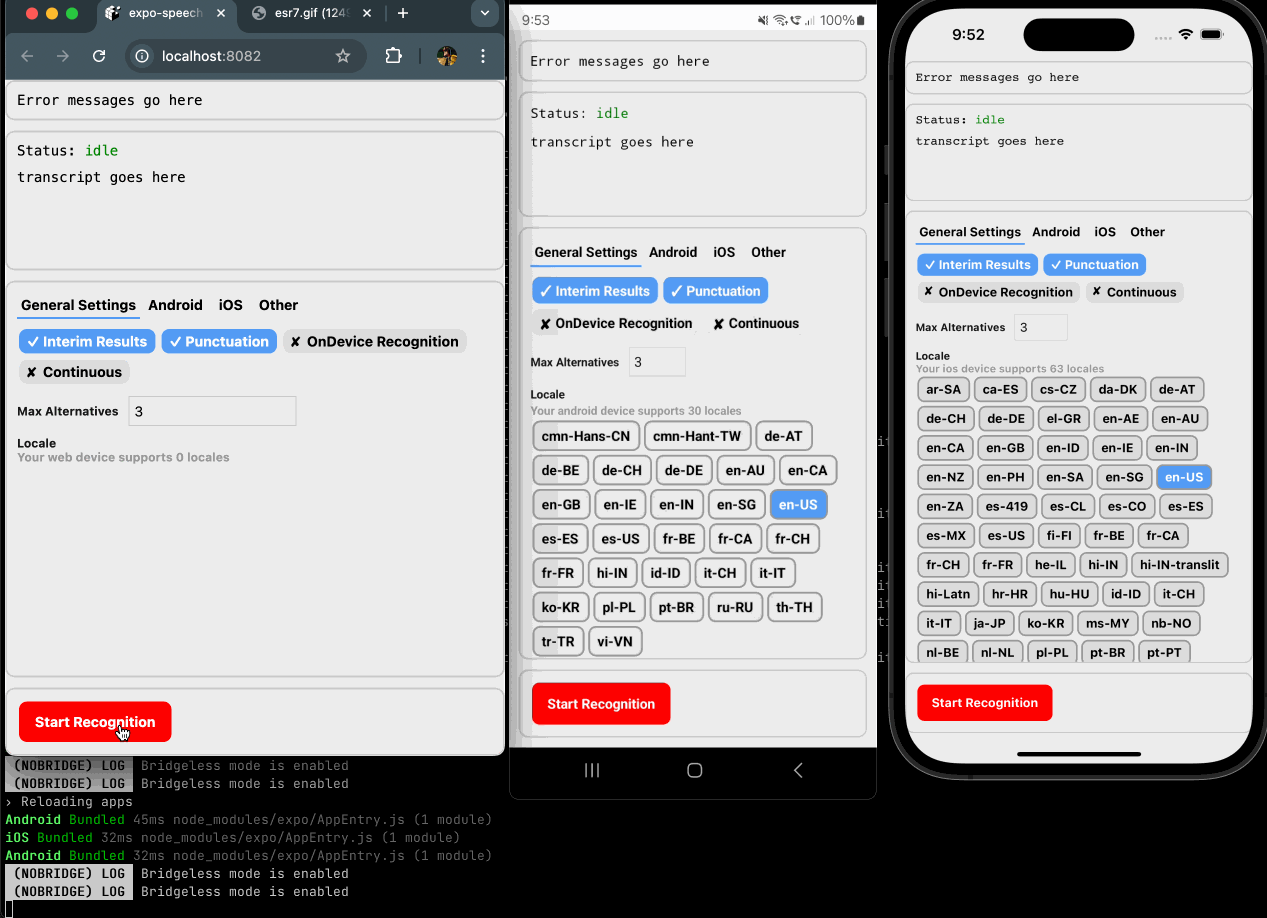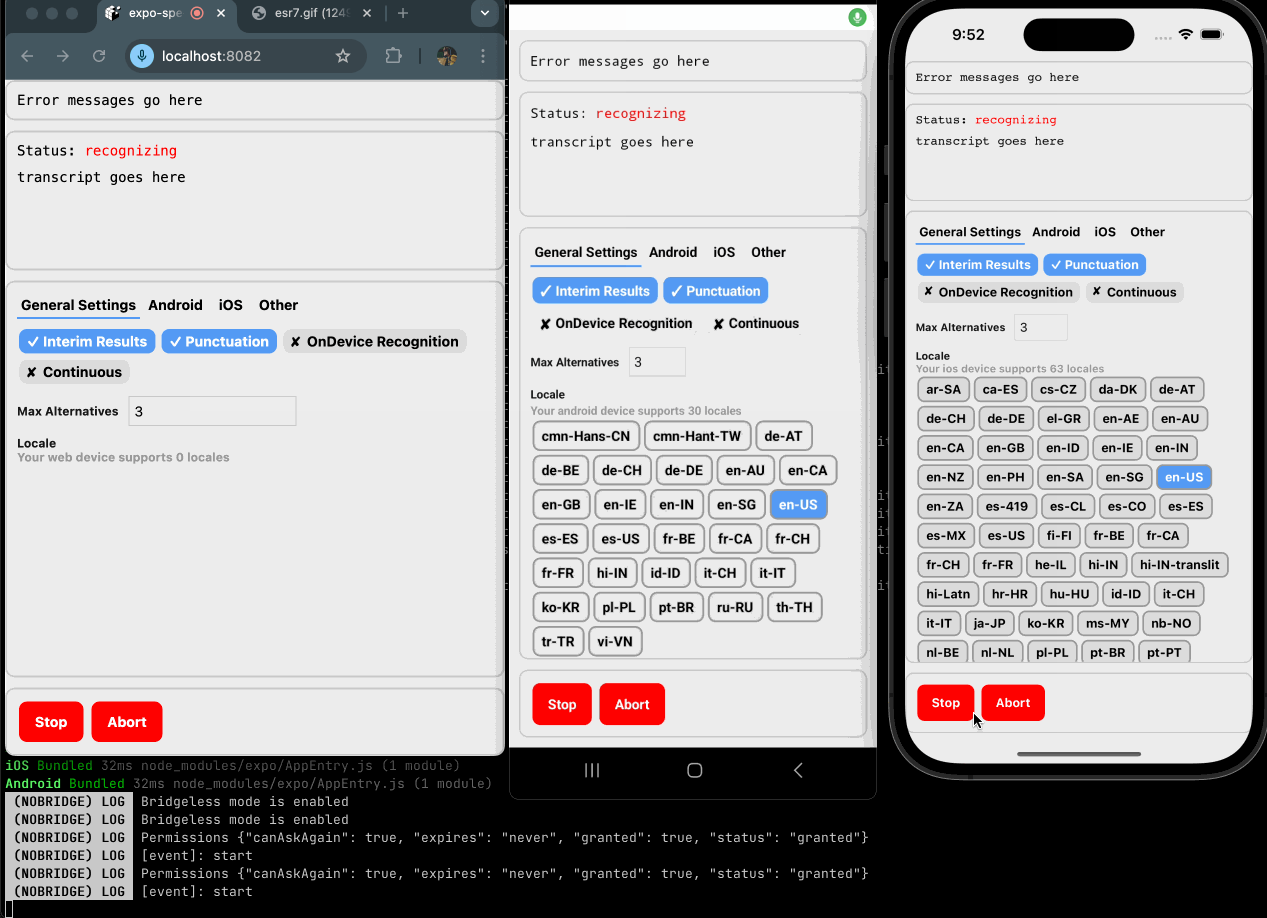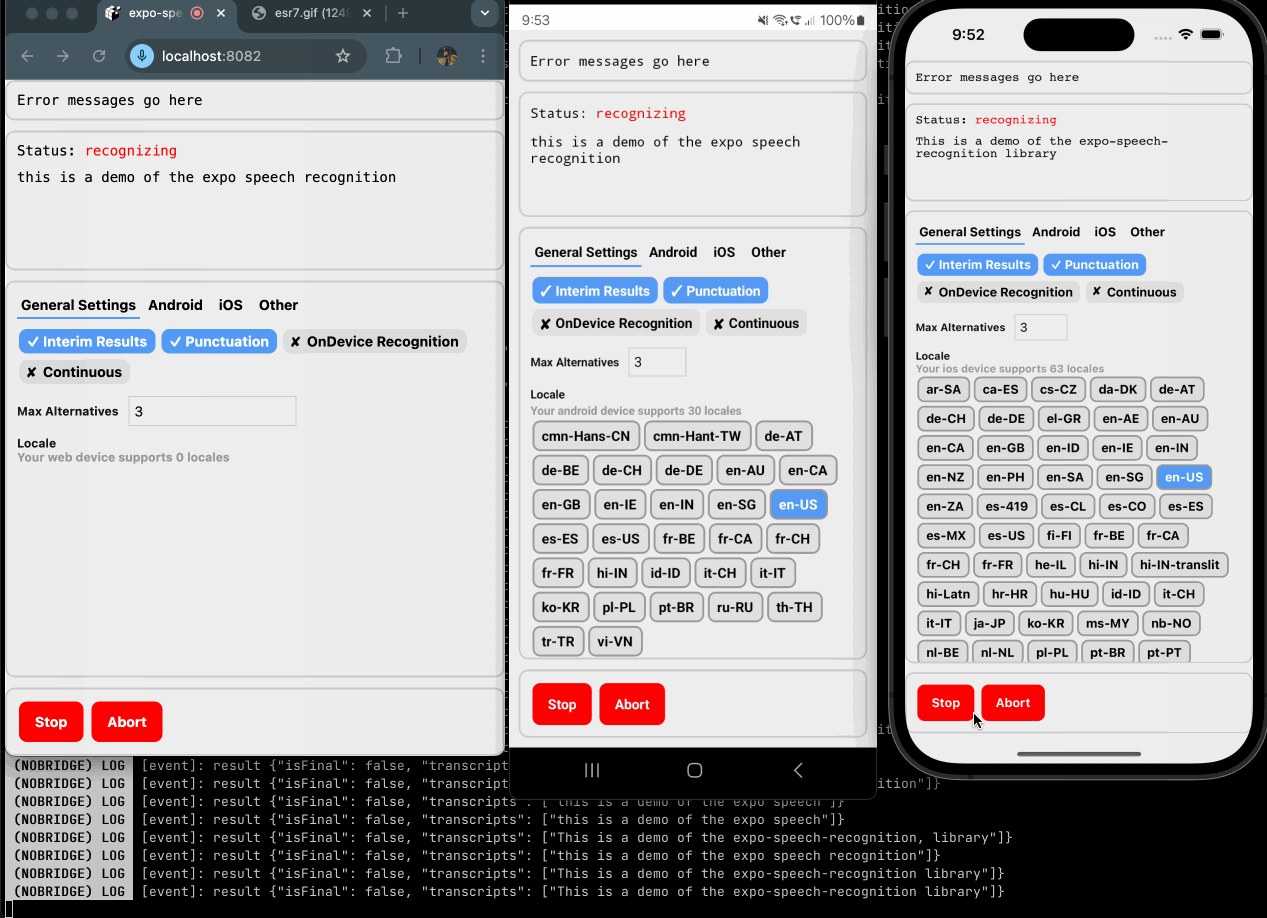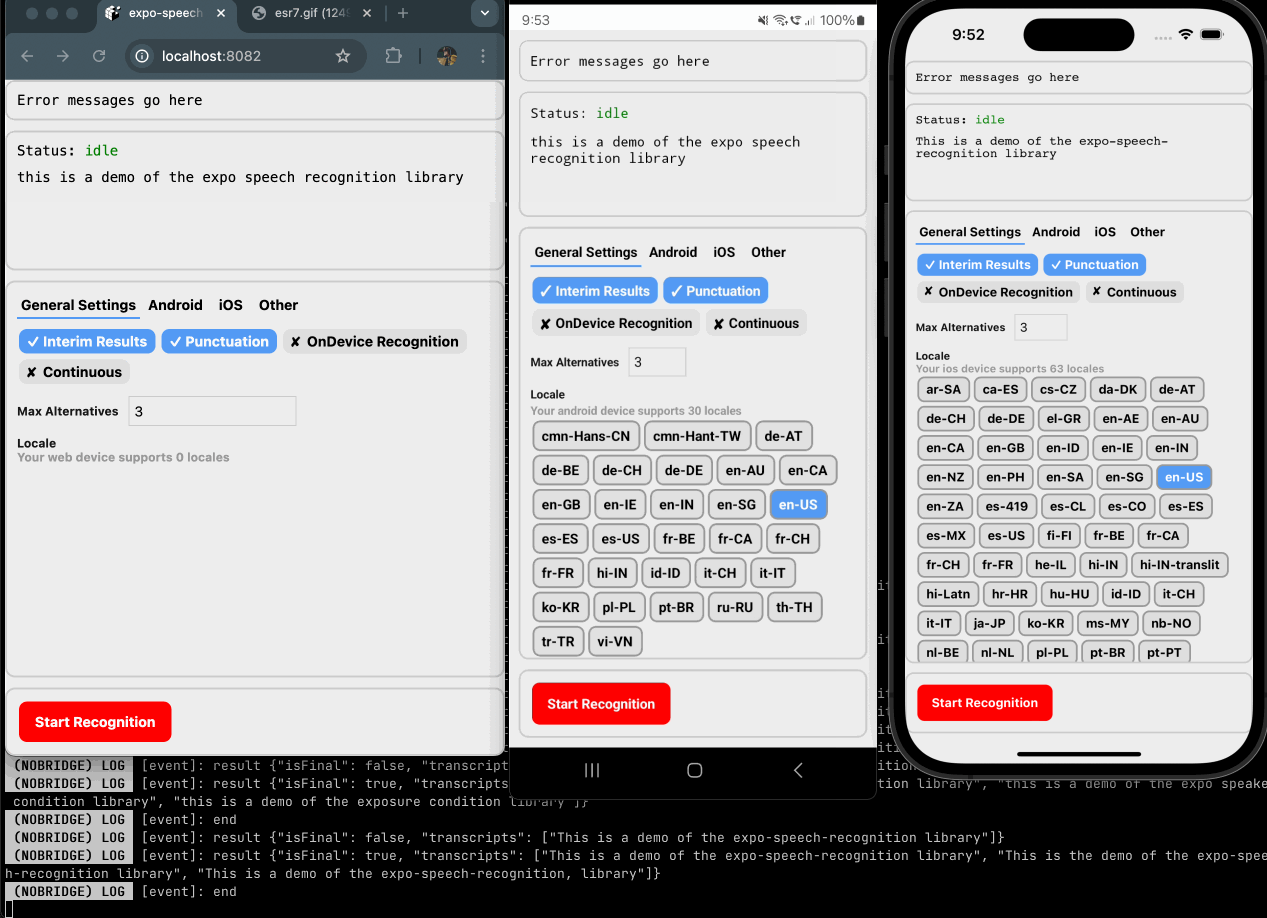
expo-speech-recognition implements the iOS SFSpeechRecognizer, Android SpeechRecognizer and Web SpeechRecognition for React Native projects with the goal of code reuse across web and mobile.
- Install the package
npm install @jamsch/expo-speech-recognition
- Configure the config plugin.
The config plugin updates the Android App Manifest to include package visibility filtering for
com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox(Google's Speech Recognition) along with the required permissions for Android and iOS.
// app.json
{
"expo": {
"plugins": [
[
"@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition",
{
"microphonePermission": "Allow $(PRODUCT_NAME) to use the microphone.",
"speechRecognitionPermission": "Allow $(PRODUCT_NAME) to use speech recognition.",
// Add additional speech service packages here that aren't listed
// under the `forceQueryable` section when running the command:
// "adb shell dumpsys package queries"
// default: ["com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox"]
"androidSpeechServicePackages": ["com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox"]
}
]
]
}
}Using hooks is the easiest way to get started. The useSpeechRecognitionEvent hook allows you to register native event listeners.
import {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule,
useSpeechRecognitionEvent,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
function App() {
const [recognizing, setRecognizing] = useState(false);
const [transcript, setTranscript] = useState("");
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("start", () => setRecognizing(true));
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("end", () => setRecognizing(false));
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("result", (event) => {
setTranscript(event.results[0].transcript);
});
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("error", (event) => {
console.log("error code:", event.error, "error messsage:", event.message);
});
const handleStart = () => {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.requestPermissionsAsync().then((result) => {
if (!result.granted) {
console.warn("Permissions not granted", result);
return;
}
// Start speech recognition
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start({
lang: "en-US",
interimResults: true,
maxAlternatives: 1,
continuous: false,
requiresOnDeviceRecognition: false,
addsPunctuation: false,
contextualStrings: ["Carlsen", "Nepomniachtchi", "Praggnanandhaa"],
});
});
};
return (
<View>
{recognizing ? (
<Button title="Start" onPress={handleStart} />
) : (
<Button title="Stop" onPress={ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.stop} />
)}
<ScrollView>
<Text>{transcript}</Text>
</ScrollView>
</View>
);
}You should request permissions prior to starting recognition. This library exports two functions: getPermissionsAsync and requestPermissionsAsync for this purpose. If you do not request permissions or the user has denied permissions after starting, expect an error event with the error code set to not-allowed.
import { ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.getPermissionsAsync().then((result) => {
console.log("Status:", result.status);
console.log("Granted:", result.granted);
console.log("Can ask again:", result.canAskAgain);
console.log("Expires:", result.expires);
});
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.requestPermissionsAsync().then((result) => {
if (!result.granted) {
console.warn("Permissions not granted", result);
return;
}
// Permissions granted! Start speech recognition, or at some other time...
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start({ lang: "en-US" });
});You can also use the ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule to use the native APIs directly. The listener events are similar to the Web Speech API.
import {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule,
addSpeechRecognitionListener,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
// Register event listeners
const startListener = addSpeechRecognitionListener("start", () => {
console.log("Speech recognition started");
});
// and remove the listener when you're done:
startListener.remove();
const endListener = addSpeechRecognitionListener("end", () => {
console.log("Speech recognition ended");
});
const resultListener = addSpeechRecognitionListener("result", (event) => {
// Note: this is not the same as the `result` event listener on the web speech API
// event.results is an array of results (e.g. `[{ transcript: "hello", confidence: 0.5, segments: [] }]`)
console.log("results:", event.results, "final:", event.isFinal);
});
const errorListener = addSpeechRecognitionListener("error", (event) => {
console.log("error code:", event.error, "error messsage:", event.message);
});
// Start speech recognition
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start({
lang: "en-US",
// Whether to return results as they become available without waiting for the final result.
interimResults: true,
// The maximum number of alternative transcriptions to return.
maxAlternatives: 1,
// Continuous recognition. Note: if false on iOS, recognition will run until no speech is detected for 3 seconds
continuous: true,
// [Default: false] Prevent device from sending audio over the network. Only enabled if the device supports it.
requiresOnDeviceRecognition: false,
// [Default: false] Include punctuation in the recognition results. This applies to full stops and commas.
addsPunctuation: false,
// [Default: undefined] Short custom phrases that are unique to your app.
contextualStrings: ["Carlsen", "Nepomniachtchi", "Praggnanandhaa"],
// [Default: undefined] Android-specific options to pass to the recognizer.
androidIntentOptions: {
EXTRA_SPEECH_INPUT_COMPLETE_SILENCE_LENGTH_MILLIS: 10000,
EXTRA_MASK_OFFENSIVE_WORDS: false,
},
// [Default: undefined] The package name of the speech recognition service to use.
androidRecognitionServicePackage: "com.google.android.tts",
// [Default: unspecified] The type of speech recognition being performed.
iosTaskHint: "unspecified", // "unspecified" | "dictation" | "search" | "confirmation"
// [Default: undefined] The audio session category and options to use.
iosCategory: {
category: "playAndRecord",
categoryOptions: ["defaultToSpeaker", "allowBluetooth"],
mode: "measurement",
},
// [Default: undefined] Recording options for Android & iOS
// For Android, this is only supported on Android 13 and above.
recordingOptions: {
// [Default: false] Whether to persist the audio to a local file path.
persist: false,
// [Default: FileSystem.CacheDirectory]
// Changes the default storage location for the audio file.
// e.g. `FileSystem.documentDirectory` (from `expo-file-system`)
outputDirectory: undefined,
// [Default: `"recording_${timestamp|uuid}.[wav|caf]"`]
// Changes the file name for the audio file.
// (you can retrieve the file path using `event.uri` on the `audiostart`/`audioend` events)
outputFileName: "recording.wav",
// [Default: undefined] The sample rate of the output audio file.
// Only supported on iOS
// Default sample rate is: 16000 on Android, 44100/48000 on iOS
outputSampleRate: undefined,
// [Default: undefined] The encoding of the output audio file.
// Only supported on iOS
outputEncoding: undefined,
},
// [Default: undefined] Use for file-based transcription.
audioSource: {
/** Local file URI, e.g. "file:///path/to/audio.wav" */
uri: undefined,
// [Android only] The number of channels in the source audio.
audioChannels: 1,
// [Android only] A value from AudioFormat - https://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/AudioFormat
audioEncoding: AudioEncodingAndroid.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT,
// [Android only] Audio sampling rate in Hz.
sampleRate: 16000,
// [Android only] The delay between chunks of audio to stream to the speech recognition service.
// Use this setting to avoid being rate-limited when using network-based recognition.
// Default: 50ms for network-based recognition, 15ms for on-device recognition
chunkDelayMillis: undefined,
},
});
// Stop capturing audio (and emit a final result if there is one)
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.stop();
// Immediately cancel speech recognition (does not process the final result)
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.abort();Events are largely based on the Web Speech API. The following events are supported:
| Event Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
audiostart |
Audio capturing has started | Includes the uri if recordingOptions.persist is enabled. |
audioend |
Audio capturing has ended | Includes the uri if recordingOptions.persist is enabled. |
end |
Speech recognition service has disconnected. | This should be the last event dispatched. |
error |
Fired when a speech recognition error occurs. | You'll also receive an error event (with code "aborted") when calling .abort()
|
nomatch |
Speech recognition service returns a final result with no significant recognition. | You may have non-final results recognized. This may get emitted after cancellation. |
result |
Speech recognition service returns a word or phrase has been positively recognized. | On Android, continous mode runs as a segmented session, meaning when a final result is reached, additional partial and final results will cover a new segment separate from the previous final result. On iOS, you should expect one final result before speech recognition has stopped. |
speechstart |
Fired when any sound — recognizable speech or not — has been detected | On iOS, this will fire once in the session after a result has occurred |
speechend |
Fired when speech recognized by the speech recognition service has stopped being detected. | Not supported yet on iOS |
start |
Speech recognition has started | Use this event to indicate to the user when to speak. |
To handle errors, you can listen to the error event:
import {
type ExpoSpeechRecognitionErrorCode,
addSpeechRecognitionListener,
useSpeechRecognitionEvent,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
addSpeechRecognitionListener("error", (event) => {
console.log("error code:", event.error, "error messsage:", event.message);
});
// or through the `useSpeechRecognitionEvent` hook
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("error", (event) => {
console.log("error code:", event.error, "error messsage:", event.message);
});
// or through the `ExpoSpeechRecognitionErrorCode` type
const error: ExpoSpeechRecognitionErrorCode = "audio-capture";The error code is largely based on the Web Speech API error codes.
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
aborted |
The user called ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.abort()
|
audio-capture |
Audio recording error. |
bad-grammar |
Provided grammar is invalid. (Note: web only) |
language-not-supported |
Locale is not supported by the speech recognizer. |
network |
Network communication required for completing the recognition failed. |
no-speech |
No final speech was detected. |
not-allowed |
Permission to use speech recognition or microphone was not granted. |
service-not-allowed |
Recognizer is unavailable. |
busy |
The recognizer is busy and cannot accept any new recognition requests. |
client |
(Android) Unknown error. Corresponds with SpeechRecognizer.ERROR_CLIENT. |
If you would like to persist the recognized audio for later use, you can enable the recordingOptions.persist option when calling start(). Enabling this setting will emit an { uri: string } event object in the audiostart and audioend events with the local file path.
Note: For Android, this is only supported on Android 13 and above. Call
supportsRecording()to see if it's available before using this feature.
Default audio output formats:
| Platform | Output Format | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Android | Linear PCM (16000 Hz, mono) | Suitable for processing on various external services (such as Google Speech API, Whisper, Deepgram, etc) |
| iOS | 32-bit Float PCM (44100/48000* Hz, mono) | Default sample rate is device specific. Change this with recordingOptions.outputSampleRate and recordingOptions.outputEncoding. |
Example:
import { Button, View } from "react-native";
import {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule,
useSpeechRecognitionEvent,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
function RecordAudio() {
const [recording, setRecording] = useState(false);
const [recordingUri, setRecordingUri] = useState<string | null>(null);
const handleStart = () => {
setRecording(true);
// Start recording
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start({
lang: "en-US",
recordingOptions: {
persist: true,
// Optional: Specify the output file path to save the recording to
// e.g. `FileSystem.documentDirectory` (from `expo-file-system`)
outputDirectory:
"/data/user/0/expo.modules.speechrecognition.example/files",
// Optional: Specify the output file name to save the recording to
outputFileName: "recording.wav",
// Optional: Specify the output sample rate to save the recording to
// Only supported on iOS
// Default sample rate: 16000 on Android, 44100/48000 on iOS
outputSampleRate: 16000,
// Optional: Specify the output encoding to save the recording to
// Only supported on iOS
// Default encoding: pcmFormatInt16 on Android, pcmFormatFloat32 on iOS
outputEncoding: "pcmFormatInt16",
},
});
};
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("audiostart", (event) => {
// Note: don't use this file until the "audioend" event is emitted
// Note: event.uri will be null if `recordingOptions.persist` is not enabled
console.log("Recording started for file:", event.uri);
});
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("audioend", (event) => {
// Recording ended, the file is now safe to use
console.log("Local file path:", event.uri);
// Android: Will be saved as a .wav file
// e.g. "file:///data/user/0/expo.modules.speechrecognition.example/cache/recording_1720678500903.wav"
// iOS: Will be saved as a .caf file
// e.g. "file:///path/to/Library/Caches/audio_CD5E6C6C-3D9D-4754-9188-D6FAF97D9DF2.caf"
setRecordingPath(event.uri);
});
return (
<View>
<Button title="Start" onPress={handleStart} disabled={recording} />
{recordingUri && <AudioPlayer source={recordingUri} />}
</View>
);
}
// AudioPlayer.tsx
import { Button } from "react-native";
import { useAudioPlayer } from "expo-audio";
function AudioPlayer(props: { source: string }) {
const player = useAudioPlayer(props.source);
return <Button title="Play" onPress={player.play} />;
}You can use the audioSource.sourceUri option to transcribe audio files instead of using the microphone.
Important notes:
- On Android, this feature is only supported on Android 13 and above. The speech recognition module will dispatch an
errorevent with the codeaudio-captureif the device doesn't support audio source transcription.- On Android, this feature is only verified to work with 16000hz 16bit PCM audio files. See here for an example audio file that works for Android and the ffmpeg command used.
- On iOS, this feature is only verified to work with 16000hz 16bit PCM WAV files and 16000hz MP3 files. See here for a list of example audio files that work for iOS (excluding the .ogg file).
The following audio formats have been verified on a Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra on Android 14:
- 16000hz 16-bit 1-channel PCM WAV
- 16000hz MP3 1-channel
- 16000hz MP3 2-channel
- 16000hz ogg vorbis 1-channel
Due to a limitation in the underlying
SFSpeechURLRecognitionRequestAPI, file-based transcription will only transcribe the first 1 minute of the audio file.
The following audio formats have been verified on an iPhone 15 Pro Max on iOS 17.5:
- 16000hz 16-bit 1-channel PCM WAV
- 16000hz MP3 1-channel
import { Button, View } from "react-native";
import {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule,
useSpeechRecognitionEvent,
AudioEncodingAndroid,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
function TranscribeAudioFile() {
const [transcription, setTranscription] = useState("");
const handleTranscribe = () => {
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start({
lang: "en-US",
interimResults: true,
audioSource: {
/** Local file URI */
uri: "file:///path/to/audio.wav",
/** [Android only] The number of channels in the source audio. */
audioChannels: 1,
/** [Android only] A value from AudioFormat - https://developer.android.com/reference/android/media/AudioFormat */
audioEncoding: AudioEncodingAndroid.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT,
/** [Android only] Audio sampling rate in Hz. */
sampleRate: 16000,
/**
* [Android only] The delay between chunks of audio to stream to the speech recognition service.
* Use this setting to avoid being rate-limited when using network-based recognition.
* If you're using on-device recognition, you may want to increase this value to avoid unprocessed audio chunks.
* Default: 50ms for network-based recognition, 15ms for on-device recognition
*/
chunkDelayMillis: undefined,
},
});
};
useSpeechRecognitionEvent("result", (ev) => {
// Note: multiple final results will likely be returned on Android
// so you'll need to concatenate previous final results
setTranscription(ev.results[0]?.transcript || "");
});
return (
<View>
<Button title="Transcribe" onPress={handleTranscribe} />
<Text>{transcription}</Text>
</View>
);
}Note: this is intended for projects that rely on third party libraries that use the Web Speech API. If you're using this library directly, you should use the Direct Module API instead.
If you intend to polyfill the webkitSpeechRecognition or SpeechRecognition globals for use with external libraries, you can use the ExpoWebSpeechRecognition class to do so.
Refer to the SpeechRecognition MDN docs for usage. Note that some features (such as grammars) on some OSes aren't yet supported.
// Import this polyfill for typings, as needed
// "npm install -D @types/dom-speech-recognition"
import "dom-speech-recognition";
import { ExpoWebSpeechRecognition } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
// Polyfill the globals for use in external libraries
webkitSpeechRecognition = ExpoWebSpeechRecognition;
SpeechRecognition = ExpoWebSpeechRecognition;
// Usage is the same as the Web Speech API..
const recognition = new ExpoWebSpeechRecognition();
recognition.lang = "en-US";
// [Default: false] Note for iOS: final results are only available after speech recognition has stopped
recognition.interimResults = true;
recognition.maxAlternatives = 1;
// [Default: false] Continuous recognition. Note: if false on iOS, recognition will run until no speech is detected for 3 seconds
recognition.continuous = true;
// Custom (non-web) properties
recognition.contextualStrings = ["Carlsen", "Nepomniachtchi", "Praggnanandhaa"];
recognition.requiresOnDeviceRecognition = true;
recognition.addsPunctuation = true;
recognition.androidIntentOptions = {
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_MODEL: "quick_response",
};
recognition.androidRecognitionServicePackage = "com.google.android.tts";
// Assign an event listener (note: this overwrites all event listeners)
recognition.onstart = (event) => console.log("started!");
recognition.onend = (event) => console.log("ended!");
recognition.onresult = (event) => {
console.log(
"result:",
event.results[event.resultIndex][0].transcript,
"final:",
event.results[event.resultIndex][0].isFinal,
);
};
// Or register an event listener
const handleStart = (event: Event) => console.log("started!");
recognition.registerEventListener("start", handleStart);
// and remember to unregister after you're done:
recognition.unregisterEventListener("start", handleStart);
const handleResult = (event: SpeechRecognitionEvent) => {
console.log("result:", event.results[event.resultIndex][0].transcript);
};
recognition.registerEventListener("result", handleResult);
recognition.registerEventListener("error", (event) => {
console.log("error code:", event.error, "error messsage:", event.message);
});
recognition.registerEventListener("end", (event) => console.log("ended!"));
// Start speech recognition
recognition.start();
// Stop speech recognition
recognition.stop();
// Immediately cancel speech recognition
recognition.abort();You may notice that after saying single words, letters, or numbers (e.g. "a", "b", 1, 5, etc.) that the speech recognition service may not return any results until you speak further. In order to improve the accuracy of single-word prompts for Android and iOS, you have the following options:
- For iOS, you can use the
iosTaskHintoption and set it toconfirmation. - For Android, you can change the language model to web_search by adding
androidIntentOptions: { EXTRA_LANGUAGE_MODEL: "web_search" }toExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.start(...). This seems to be superior over the defaultfree_formmodel for single-word prompts. - For both platforms, you may want to consider using on-device recognition. On-device recognition tends to process smaller chunks of audio and is more responsive.
- Alternatively, you may want to consider recording the recognized audio and sending it to an external service for further processing. See Persisting Audio Recordings for more information. Note that some services (such as the Google Speech API) may require an audio file with a duration of at least 3 seconds.
As of 7 Aug 2024, the following platforms are supported:
| Platform | Supported | Default Recognition Engine | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android (React Native) | ✅ | Recording feature is only supported on Android 13 and above. Recognition engine can be changed via androidRecognitionServicePackage
|
|
| iOS (React Native) | ✅ | Siri | |
| Chrome Desktop | ✅ | Google (server-based) | Implemented via prefix webkitSpeechRecognition. |
| Safari Desktop >= v16 | ✅ | Siri | Implemented via prefix webkitSpeechRecognition. Siri needs to be enabled |
| Chrome on Android | ✅ | There's a few differences in how results get handled in comparison to the Chrome Desktop implementation | |
| Chrome on iOS | ❌ | Not working (Last tested 2023) | |
| Edge on Windows | (unknown) | Azure | SpeechRecognition API is implemented, but requires the Azure speech component. Verify it’s presence at edge://components
|
| Edge on Mac ARM | ❌ | Azure | SpeechRecognition API is implemented, but requires the Azure speech component. Verify it’s presence at edge://components
|
| Brave Desktop | ❌ | - | As of Aug 2024, Brave is working on an implementation however there's currently no ETA (source: brave-browser/issues/3725) |
| Firefox Desktop | ❌ | - | No SpeechRecognition implementation |
Get the list of supported locales and the installed locales that can be used for on-device speech recognition.
import { getSupportedLocales } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
getSupportedLocales({
/**
* The package name of the speech recognition service to use.
* If not provided, the default service used for on-device recognition will be used.
*
* Warning: the service package (such as Bixby) may not be able to return any results.
*/
androidRecognitionServicePackage: "com.google.android.as",
})
.then((supportedLocales) => {
console.log("Supported locales:", supportedLocales.locales.join(", "));
// The on-device locales for the provided service package.
// Likely will be empty if it's not "com.google.android.as"
console.log(
"On-device locales:",
supportedLocales.installedLocales.join(", "),
);
})
.catch((error) => {
// If the service package is not found
// or there was an error retrieving the supported locales
console.error("Error getting supported locales:", error);
});Get list of speech recognition services available on the device.
Note: this only includes services that are listed under
androidSpeechServicePackagesin your app.json as well as the core services listed underforceQueryablewhen running the command:adb shell dumpsys package queries
import { getSpeechRecognitionServices } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const packages = ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.getSpeechRecognitionServices();
console.log("Speech recognition services:", packages.join(", "));
// e.g. ["com.google.android.as", "com.google.android.tts", "com.samsung.android.bixby.agent"]Returns the default voice recognition service on the device.
import { getDefaultRecognitionService } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const service = ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.getDefaultRecognitionService();
console.log("Default recognition service:", service.packageName);
// Usually this is "com.google.android.as" for Android 12+ and "com.google.android.tts" for older Android versionsReturns the default voice assistant service on the device.
import { getAssistantService } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const service = ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.getAssistantService();
console.log("Default assistant service:", service.packageName);
// Usually "com.google.android.googlequicksearchbox" for Google
// or "com.samsung.android.bixby.agent" for SamsungWhether on-device speech recognition is available on the device.
import { supportsOnDeviceRecognition } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const available = supportsOnDeviceRecognition();
console.log("OnDevice recognition available:", available);Whether audio recording is supported during speech recognition. This mostly applies to Android devices, to check if it's at least Android 13.
import { supportsRecording } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const available = supportsRecording();
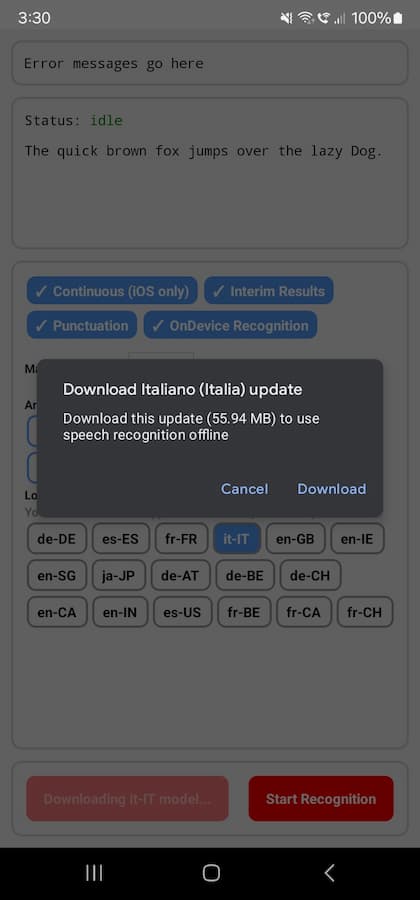
console.log("Recording available:", available);API: androidTriggerOfflineModelDownload({ locale: string }): Promise<{ status: "opened_dialog" | "download_success" | "download_canceled", message: string }>
Users on Android devices will first need to download the offline model for the locale they want to use in order to use on-device speech recognition (i.e. the requiresOnDeviceRecognition setting in the start options).
You can see which locales are supported and installed on your device by running getSupportedLocales().
To download the offline model for a specific locale, use the androidTriggerOfflineModelDownload function.
import { ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
// Download the offline model for the specified locale
ExpoSpeechRecognitionModule.androidTriggerOfflineModelDownload({
locale: "en-US",
})
.then((result) => {
switch (result.status) {
case "opened_dialog":
// On Android 13, the status will be "opened_dialog" indicating that the model download dialog was opened.
console.log("Offline model download dialog opened.");
break;
case "download_success":
// On Android 14+, model was succesfully downloaded.
console.log("Offline model downloaded successfully!");
break;
case "download_canceled":
// On Android 14+, the download was canceled by a user interaction.
console.log("Offline model download was canceled.");
break;
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log("Failed to download offline model!", err.message);
});The device will display a dialog to download the model. Once the model is downloaded, you can use the getSupportedLocales function to get the list of installed locales.
This function is an implementation of AVAudioSession.setCategory for iOS. For multimedia applications, you may want to set the audio session category and mode to control the audio routing.
Note: when starting speech recognition, audio session category is changed to
playAndRecordwith optiondefaultToSpeakerandallowBluetoothand modemeasurement. You can instead configure the audio session category and mode by passing theiosCategoryoption to thestartfunction.
import {
setCategoryIOS,
AVAudioSessionCategory,
AVAudioSessionCategoryOptions,
AVAudioSessionMode,
} from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
setCategoryIOS({
category: AVAudioSessionCategory.playAndRecord, // or "playAndRecord"
categoryOptions: [
AVAudioSessionCategoryOptions.defaultToSpeaker,
AVAudioSessionCategoryOptions.allowBluetooth,
],
mode: AVAudioSessionMode.default,
});Returns the current audio session category and options. For advanced use cases, you may want to use this function to safely configure the audio session category and mode.
import { getAudioSessionCategoryAndOptionsIOS } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
const values = getAudioSessionCategoryAndOptionsIOS();
console.log(values);
// { category: "playAndRecord", categoryOptions: ["defaultToSpeaker", "allowBluetooth"], mode: "measurement" }Sets the audio session active state.
import { setAudioSessionActiveIOS } from "@jamsch/expo-speech-recognition";
setAudioSessionActiveIOS(true, {
notifyOthersOnDeactivation: true,
});