Proximux
Proximux is a drop in replacement for existing TCP connections.
Works with MySQL and other services that are using TCP, like OpenSearch/ElasticSearch, web services, etc.
Note! In current version Proximux expects that on every incoming request Target Server returns a response.
Table of Contents
- Configuration
- Modes
- Exchange Methods
- Messages Processing Order
- Events
- IP Blacklisting
- Examples
- Architecture
Configuration
There are 2 ways to set the configuration: through environment variables and configuration object. Number of TCP TARGETS should be the same as PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT.
Env Variables
The following configuration will setup Proximux in Proxy mode. See other modes for more details.
# Log levels: 0 -no logs, 1 - errors, 2 - info, 3 - debug
export LOG_LEVEL=1
# Local server
export LOCAL_HOST=localhost
export LOCAL_PORT=3307
# Enables ipv6Only. Possible values: 0 (false, default), 1 (true).
export LOCAL_IPV6_ONLY=0
# Maximum number of concurrent connections. Other connections will be rejected. -1 means "disabled".
export LOCAL_MAX_CONNECTIONS=-2
# Exchange
# Async possible values: 0 (false, default), 1 (true).
export EXCHANGE_FUNNEL_ASYNC=0
# Pool
# Inactivity, in msec. -1 means "disabled".
export PROXY_INACTIVE_TIMEOUT=-1
# Should be equal to the number of TCP TARGETS below.
export PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT=2
# TCP TARGETS
export TARGET_HOST_1=target.host
export TARGET_PORT_1=4441
export TARGET_CONN_1_KEEP_ALIVE=0
export TARGET_HOST_2=target.host
export TARGET_PORT_2=4441
export TARGET_CONN_2_KEEP_ALIVE=0Config Object
// warmup will connect all TCP Targets first
const warmup = false;
const configObj = {
logLevel: 1,
localServerHost: 'localhost',
localServerPort: 3307,
localServerIpv6Only: false,
localServerMaxConnections: 2,
exchangeFunnelAsync: false,
targetServers: [
{
host: 'target.host',
port: 4441,
keepAlive: false,
},
{
host: 'target.host',
port: 4441,
keepAlive: false,
}
],
proxyConnectionsCount: 2,
proxyInactivityTimeout: -1,
};
const app = new Proximux(warmup, configObj);
app.run();Modes
Proximux works in one of the 3 possible modes:
- Proxy
- Multiplexer FIFO
- Multiplexer Funnel
Proxy Mode
Using a Proxy Mode is similar to using a direct connection to the Target Server.
To setup this mode, set the number on incoming connections (LOCAL_MAX_CONNECTIONS)
to be equal to the number of target connections (PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT).
| Incoming connections | Outgoing connections |
|---|---|
| -------> | -------> |
| -------> | -------> |
It's possible to add connection interceptor to validate incoming IP address or handle request/response to the server. In this mode Exchange uses a "piped" exchange method (see (Exchange Methods)[#exchange-methods]). Useful to handle incoming and outgoing events.
FIFO Mode (Multiplexer With Single Target)
Incoming messages are buffering and processing in a FIFO (first in, first out) queue.
| Incoming connections | Outgoing connections |
|---|---|
| -------> | |
| -------> | -------> |
| -------> |
To enable FIFO, set env PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT=1.
LOCAL_MAX_CONNECTIONS should NOT be 1 (otherwise it will enable PROXY mode).
In this mode connections are multiplexed and Target Server handles a single connection instead of many. In this mode Exchange uses a "detached" exchange method (see Exchange Methods). It can be useful in a few cases, for example, to overcome the Target Server connection limit.
Funnel Mode (Multiplexer With Multiple Targets)
| Incoming connections | Outgoing connections |
|---|---|
| -------> | |
| -------> | -------> |
| -------> | -------> |
| -------> |
This is the setup when PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT is set to greater than 1.
Also LOCAL_MAX_CONNECTIONS should not match PROXY_CONNECTIONS_CNT (otherwise it will be a PROXY mode).
In this mode Exchange uses a "detached" exchange method (see Exchange Methods).
Exchange Methods
Exchange methods:
- Detached (event based). Stateless, event-based exchange. Used in FiFO and Funnel modes.
- Piped (also forwards socket options to upstream socket). Used in Proxy mode. Don't use this type, until target server rely on socket options.
Note! With Piped exchange method, malformed connections may force Upstream for disconnecting/reconnecting from Target Server. Which may significantly slow down the request/response processing time. It is recommended to use Piped method inside local network to mitigate risk of intentional malformed requests. Also see IP Blacklisting section to see how to protect your setup.
Messages Processing Order
Messages processing order:
- In FIFO mode all events are processing in order of receiving.
- In Proxy mode, order guarantee is not controlled by Proximux. Each connection may process events synchronously or asynchronously, depends on Client and Target Server setup.
- In Funnel mode by default each upstream connection process incoming requests sequentially and synchronously (but in non-blocking to other connections way).
Note! In Funnel mode it is possible to switch to async processing. In this case there is no guaranty that response will match to the request, as Target Server may respond first with event that takes less time to process. To set Funnel to "async", update
EXCHANGE_FUNNEL_ASYNC=1.
Events
Currently possible events are:
- "connected". New client connected to the Local Server.
- "request". Client sent a request.
All callbacks are processing synchronously.
// Events Callbacks
connected: (logger: Logger, remote: Partial<AddressInfo>) => void;
request: (logger: Logger, data: Buffer, response: Promise<Buffer>) => void;See example below of how to add your own listeners.
// Throwing Error in "connected" event will close new connection without further data processing.
const app = new Proximux(false);
app.getEventEmitter().on('connected', (logger, remote) => {
const remoteIp = remote?.address || '';
// ...
});app.getEventEmitter().on('request', (logger, rawReq, rawRespPromise) => {
const t1 = new Date();
rawRespPromise.then(() => {
const time = new Date().getTime() - t1.getTime();
logger.debug({
msg: 'Data interceptor',
req: rawReq,
time,
});
}).catch((err) => logger.error(err));
});IP Blacklisting
app.getEventEmitter().on('connected', (logger, remote) => {
const remoteIp = remote?.address || '';
const remoteType = remote?.family?.toLowerCase() === 'ipv6' ? 'ipv6' : 'ipv4';
const blockList = new net.BlockList();
blockList.addAddress('123.123.123.123');
if (blockList.check(remoteIp, remoteType)) {
throw new Error('IP is blacklisted');
}
logger.debug('Blocklist check passed');
});Examples
MySQL
See this docker-based example.
User auth in MySQL is done through socket options, so the only possible configuration mode is "Proxy".
Example shows:
- Connections intercepting.
- Blocking IP addresses with BlockList.
- Query logging.
- Response time logging.
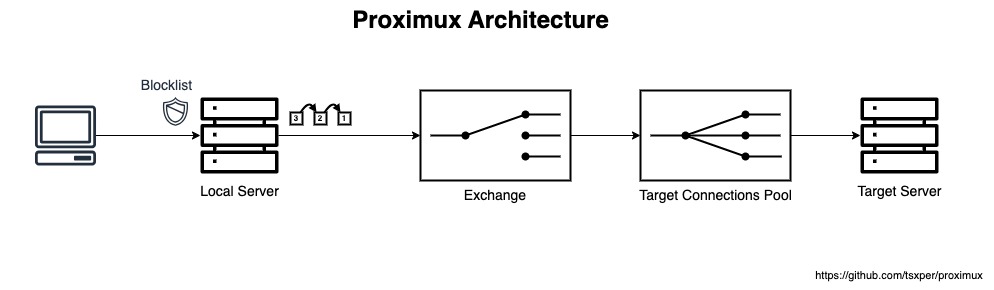
Architecture
- Local Server. It is a server that handles incoming connections.
- Exchange. Pass and receive data between connections.
- Pool. Manage outgoing connections (connections to the Target Server).
- Target Connection. Connection to the Target Server (Upstream).
- Target Server. Your connection target.