Azure Mixed Reality Authentication client library for JavaScript
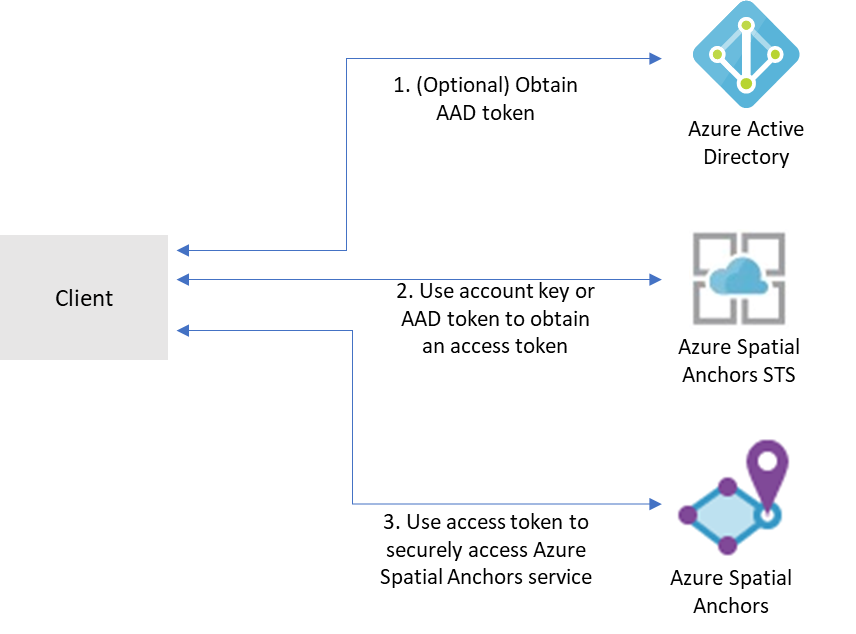
Mixed Reality services, like Azure Spatial Anchors, Azure Remote Rendering, and others, use the Mixed Reality security token service (STS) for authentication. This package supports exchanging Mixed Reality account credentials for an access token from the STS that can be used to access Mixed Reality services.
Key links:
Getting started
Currently supported environments
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription.
- You must have an account with an Azure Mixed Reality service:
- Familiarity with the authentication and credential concepts from the Azure Identity library.
Install the @azure/mixed-reality-authentication package
Install the Azure Mixed Reality Authentication client library for JavaScript with npm:
npm install @azure/mixed-reality-authentication
Create and authenticate a MixedRealityStsClient
To create a client object to request an access token for a Mixed Reality service, you will need the account identifier
and account domain of your Mixed Reality service resource and a credential.
Mixed Reality services support a few different forms of authentication:
- Account Key authentication
- Account keys enable you to get started quickly with using Mixed Reality services. But before you deploy your application to production, we recommend that you update your app to use Azure AD authentication.
- Azure Active Directory (AD) token authentication
- If you're building an enterprise application and your company is using Azure AD as its identity system, you can use user-based Azure AD authentication in your app. You then grant access to your Mixed Reality accounts by using your existing Azure AD security groups. You can also grant access directly to users in your organization.
- Otherwise, we recommend that you obtain Azure AD tokens from a web service that supports your app. We recommend this method for production applications because it allows you to avoid embedding the credentials for access to a Mixed Reality service in your client application.
See here for detailed instructions and information.
Using account key authentication
Use the Azure Portal to browse to your Mixed Reality service resource and retrieve an account key.
Once you have an account key, you can use the AzureKeyCredential class to authenticate the client as follows:
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
const { MixedRealityStsClient } = require("@azure/mixed-reality-authentication");
const accountId = "<ACCOUNTD ID>";
const accountDomain = "<ACCOUNT_DOMAIN>";
const accountKey = "<ACCOUNT_KEY>";
const client = new MixedRealityStsClient(
accountId,
accountDomain,
new AzureKeyCredential(accountKey)
);Note: Account key authentication is not recommended for production applications.
Using an Azure Active Directory Credential
Account key authentication is used in most of the examples, but you can also authenticate with Azure Active Directory
using the Azure Identity library. This is the recommended method for production applications. To use
the DefaultAzureCredential provider shown below, or other credential providers provided with
the Azure SDK, please install the @azure/identity package:
npm install @azure/identityYou will also need to register a new AAD application and grant access to your Mixed Reality resource by assigning the appropriate role for your Mixed Reality service to your service principal.
Set the values of the client ID, tenant ID, and client secret of the AAD application as environment variables:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID, AZURE_TENANT_ID, AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET.
const { MixedRealityStsClient } = require("@azure/mixed-reality-authentication");
const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("@azure/identity");
const client = new MixedRealityStsClient(accountId, accountDomain, new DefaultAzureCredential());Key concepts
MixedRealityStsClient
The MixedRealityStsClient is the client library used to access the Mixed Reality STS to get an access token.
Tokens obtained from the Mixed Reality STS have a lifetime of 24 hours.
Return Value
The return value for a successful call to getToken is an GetTokenResponse, which is an AccessToken from
@azure/core-http.
Examples
Retrieve an access token
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
const { MixedRealityStsClient } = require("@azure/mixed-reality-authentication");
const accountId = "<ACCOUNTD ID>";
const accountDomain = "<ACCOUNT_DOMAIN>";
const accountKey = "<ACCOUNT_KEY>";
const client = new MixedRealityStsClient(
accountId,
accountDomain,
new AzureKeyCredential(accountKey)
);
const token = await client.getToken();See the authentication examples above or Azure Identity for more complex authentication scenarios.
Using the access token in a Mixed Reality client library
Some Mixed Reality client libraries might accept an access token in place of a credential. For example:
// GetMixedRealityAccessTokenFromWebService is a hypothetical method that retrieves
// a Mixed Reality access token from a web service. The web service would use the
// MixedRealityStsClient and credentials to obtain an access token to be returned
// to the client.
const accessToken = await GetMixedRealityAccessTokenFromWebService();
const account = new SpatialAnchorsAccount(accountId, accountDomain);
const client = new SpatialAnchorsClient(account, accessToken);Note: The SpatialAnchorsClient usage above is hypothetical and may not reflect the actual library. Consult the
documentation for the client library you're using to determine if and how this might be supported.
Troubleshooting
Logging
Enabling logging may help uncover useful information about failures. In order to see a log of HTTP requests and responses, set the AZURE_LOG_LEVEL environment variable to info. Alternatively, logging can be enabled at runtime by calling setLogLevel in the @azure/logger:
import { setLogLevel } from "@azure/logger";
setLogLevel("info");For more detailed instructions on how to enable logs, you can look at the @azure/logger package docs.
Next steps
Please take a look at the samples directory for detailed examples on how to use this library.
Contributing
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA-bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., label, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
If you'd like to contribute to this library, please read the contributing guide to learn more about how to build and test the code.