React MVVM Framework
Attention!
This package is deprecated. Instead, you can use new version of this package - React VVM
It's lighter, works with several versions of React and MobX and most important - it's well documented.
It also doesn't have the Model entity, because not every React
application needs such an entity. If you need, you can just copy the
source code
of it.
A super lightweight React MVVM Framework based on using MobX and TSyringe.
In fact, this is not so much a framework as a demonstration of an approach to front-end development. I think that such a wide spread of the Flux architecture and in particular the Redux framework is not due to anything.
The main idea of this framework is that MobX + DI pattern + MVVM pattern >> Flux or/and Redux.
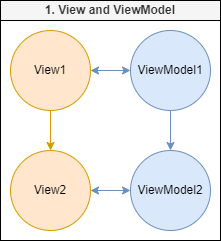
View
The View is a component which creates an instance of the ViewModel. The view pass its props
to the ViewModel and sets ViewModel's parent field - a ViewModel of parent View. . Also,
a View has an ErrorBound, which means if any child component of the View would raise an
error, View will just disappear and stop error from spreading.
Usage:
view(ViewModel)(component, makeObserver);-
ViewModel- a class, which extends fromViewModelbase class. -
component- a React-component -
makeObserver- a flag that tells whether to make a component an observer or not. By defaulttrue.
Example
import React, { VFC } from 'react';
import { view } from '@yoskutik/mobx-react-mvvm';
type SomeViewProps = {
prop1: number;
prop2?: string;
}
const SomeView: VFC<SomeViewProps> = view(SomeViewModel)(({ viewModel, prop1, prop2 }) => (
<div/>
));ChildView
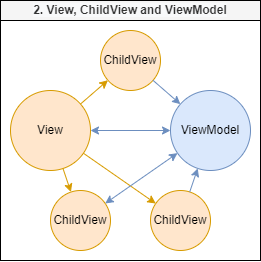
ChildView must be used somewhere inside a View. ChildView does not create an instance of a ViewModel, but it has a link to one. ChildView also has an ErrorBoundary.
Usage:
childView(component, makeObserver);-
component- a React-component -
makeObserver- a flag that tells whether to make a component an observer or not. By defaulttrue.
Example
import React from 'react';
import { childView } from '@yoskutik/mobx-react-mvvm';
import type { SomeViewModel } from './SomeViewModel';
type SomeSomeChildProps = {
prop1: number;
}
const SomeChild = childView<SomeViewModel, SomeSomeChildProps>(({ viewModel, prop1 }) => (
<div/>
));Note that is better to use import type instead of import in case you need to import
View's ViewModel type to prevent the occurrence of cyclic dependencies.
ViewModel
ViewModel is an object that should contain View's logic and observable fields.
These are fields and methods that are available for all ViewModels:
| Modifier | Description | |
|---|---|---|
viewProps |
protected readonly |
Properties that were given to a View |
onViewUnmount |
protected |
This function is called after the View has become unmounted |
onViewMount |
protected |
This function is called after the View has become mounted |
parent |
public readonly |
A link for a parent ViewModel |
isActive |
public readonly |
Flag that tell whether the View is in the virtual DOM |
The fields parent and viewProps are initialized only after the constructor has done. But
they both are observable.ref, so you can use reaction, autorun and observe in the
constructor.
The viewProps are updated every time HOC of the View is updated. Because of the HOC is
memorized they are updated every time when the properties are new.
To specify the typing of the parent and viewProps fields use generics of ViewModel class.
Every ViewModel supposed to be extended from ViewModel base class. And also they must have
a decorator @singleton or @injetable from TSyringe.
Example
import { injectable } from 'tsyringe';
import { ViewModel } from '@yoskutik/mobx-react-mvvm';
import { observable, makeObservable } from 'mobx';
import type { ParentViewModel } from './ParentViewModel';
import type { SomeViewProps } from './SomeView';
@injectable()
class SomeViewModel extends ViewModel<ParentViewModel, SomeViewProps> {
@observable count = 0;
constructor() {
super();
makeObservable(this);
}
@action add = () => this.count++;
}Note that is better to use import type instead of import in case you need to import
parent View's ViewModel type or/and View's props type to prevent the occurrence of cyclic
dependencies.
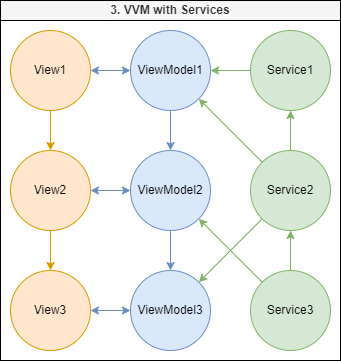
Service
Service is a class that contains general data or methods. This package does not provide
any entities to create services. But you can create them just adding @singleton or
@injetable to your classes.
Services may interact with each other and ViewModels.
Model
A model can be used when you have to validate some fields or watch have them been changed.
To create a new model you must define a new class extended from the Model base class. If you want
to validate some fields, use @validate decorator. If you want to watch for some fields changes, use
@field decorator.
import { Model, validate, field } from '@yoskutik/mobx-react-mvvm';
import { required } from './somewhereElse';
class SomeModel extends Model {
// This field will automatically validates on `field1` change. If `field1` is invalid,
// the error will appear at `errors.field1`
@validate(required())
@observable field1 = '';
@field()
@observable field2 = 1;
}
const model = SomeModel.create();
const modelWithInitialData = SomeModel.create(initialData);@validate decorator
The @validate decorator is configurable. You can pass an object to @validate or a list of validators:
@validate({
preprocess: (value, model) => any,
validators: [validator1(), validator2()],
shouldCheckValidity: (model) => boolean,
})
// Or
@validate(validator1(), validator2())Parameters:
-
preprocess- In case the value must be preprocessed before the validation. It's useful when you want to mark a string consisting of spaces to be required. -
validators- A list of validators. A validator must return a boolean or a string. If it returnsfalseit means the value is valid. If it returnstrueor a string, where's an error. String should be returned if you need to tell error's name. -
shouldCheckValidity- In case you should validate the fields depending on other field of the model, you can use this function. By default, all fields with@validatedecorator are validating.
@field decorator
The @field decorator is also configurable. You can pass an object to @field:
@field({
factory: (record) => any,
watch: boolean,
comparator: (prevValue, value, record) => boolean,
label: string,
})Parameters:
-
factory- If you want to set initial value depending on other fields or initial data, you can use this function. -
watch- A flag that tells to watch for changes of the field. By default, istrue. -
comparator- A function to compare previous and new value. By default, values are comparing by links. You can passdeepComparator()if you need to compare arrays or simple objects. -
label- An associated label for the field. Label is stored inmodel.labels[fieldName]. If there's no@fieldwithlabelargument, thelabelfield will beundefined.
Diagrams
View and ViewModel interaction
View, ChildView and ViewModel interaction
Interaction with DI
Examples
- TODO List (an example for View, ChildView and ViewModel):
- Articles reader (DI):
- Forms (Model):