npm install athmThis a library that allows you to interact with ATH Móvil from Javascript. You can send and receive money, view current balance, past transactions, available cards, and account holder information. Just install the NPM package, import it in your code, and start interacting with ATH Móvil programatically!
Self contained example to get the balance of the current account.
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
async function printBalance() {
await account.login();
let balance = await account.getBalance();
console.log(balance);
}
printBalance();Self contained example to send one dollar to an specified phone number using the default debit card.
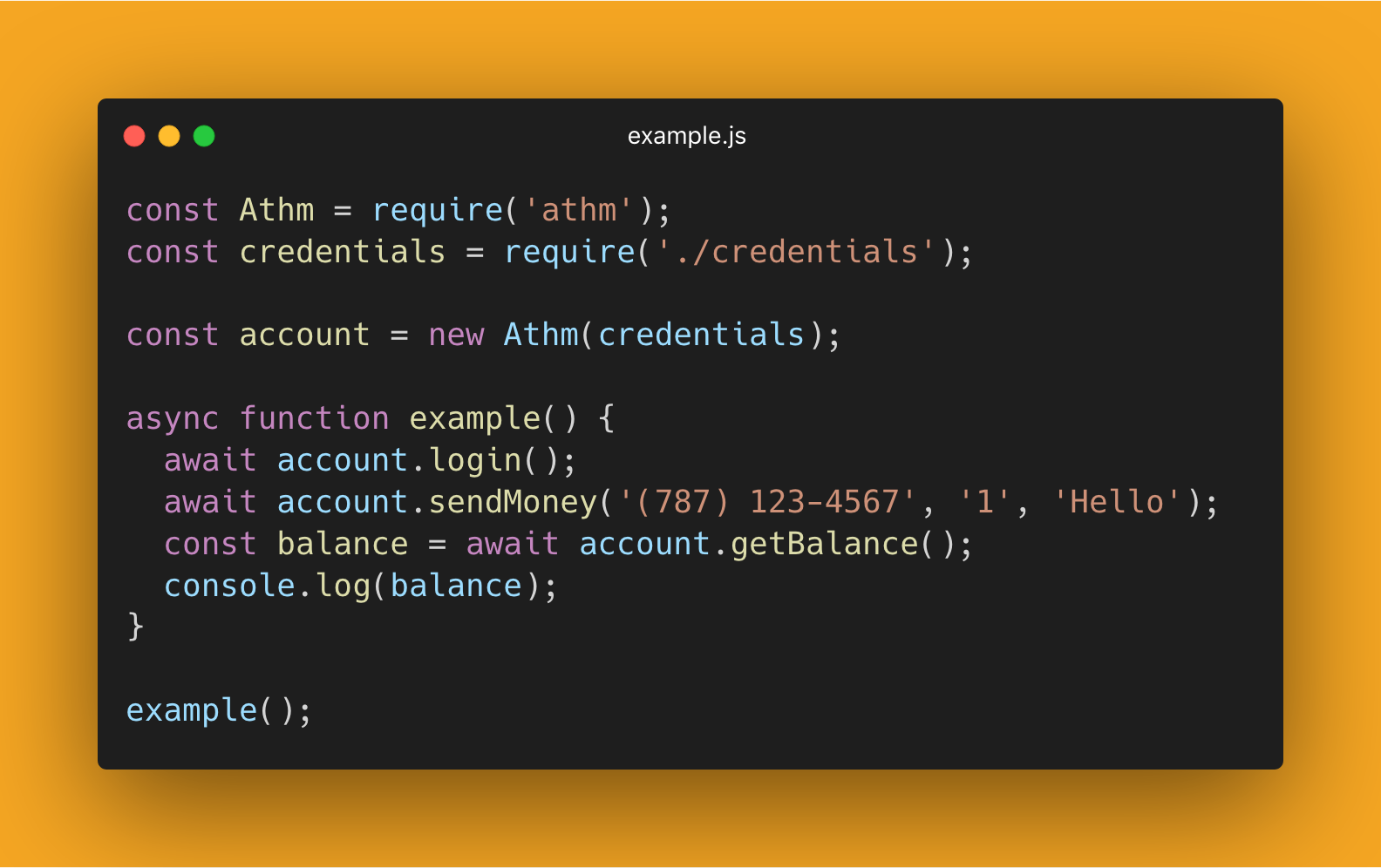
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
async function sendOneDollar() {
await account.login();
let send = await account.sendMoney('(787) 123-4567', '1', 'Hello.');
console.log(send);
}
sendOneDollar();Self contained example to get the name of the owner of the current account and the default card associated with it.
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
async function printInfo() {
await account.login();
let myName = await account.getMyName();
let defaultCard = await account.getDefaultCard();
console.log(myName);
console.log(defaultCard);
}
printInfo();Self contained example to get the name, balance and first card associated with the current account. This method, in contrast to using the other methods separately, obtains the information with a single GET request.
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
async function printInfo() {
await account.login();
let info = await account.getBasicInfo();
console.log(info);
console.log(info.name);
}
printInfo();Self contained example to get the balance of the current account. This examples uses an anonymous arrow function.
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
(async () => {
await account.login();
let balance = await account.getBalance();
console.log(balance);
})();Example on how to use most of the available methods.
const Athm = require('athm');
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}
let account = new Athm(credentials);
async function fullExample() {
let login = await account.login();
log('Login', login)
let info = await account.getBasicInfo();
log('Basic Information', info);
let cardName = await account.getFirstCardName();
log('Card Name', cardName);
let phone = await account.getMyPhone();
log('Phone Number', phone);
let email = await account.getMyEmail();
log('Email', email);
let receivedTransactions = await account.getReceivedTransactions();
log('Received Transactions', receivedTransactions);
let sentTransactions = await account.getSentTransactions();
log('Sent Transactions', sentTransactions);
let name = await account.getMyName();
log('Name', name);
let balance = await account.getBalance();
log('Balance', balance);
let defaultCard = await account.getDefaultCard();
log('Default Card', defaultCard);
// let send = await account.sendMoney('(787) 123-4567', '1', 'Hello.');
// log('Sending Money', send);
let logout = await account.logout();
log('Logout', logout);
}
// Utility function to log the information in a 'pretty' way
function log(name, object) {
let separator = '----------------------'
console.log(name + ':');
console.log(separator);
console.log(object)
console.log(separator);
console.log('\n\n\n')
}
fullExample();-
Go to the ATH Móvil configuration page and click on 'Change Security Questions'.
-
On the 'Change Security Questions' page select the questions that you want and answer them.
-
Use this list to determine the IDs of your selected questions.
-
Use these IDs to set up your credentials object like this:
const credentials = {
username: 'example@gmail.com',
password: 'myPassword123',
answers: { 'Q1.8': 'Albert', 'Q1.7': 'Saphire', 'Q1.10': 'San Juan' }
}Logs into the account. Returns true if successful.
Logs out of the current account. Returns true if successful.
All the methods prefixed with 'get' are used to fetch a page from ATH Móvil, scrape it and then return the desired content. All of these methods are asynchronous.
Returns a string with the name of the account owner.
Returns a number with the current account balance (for now only only for the first/default card)
Returns a string with the phone number associated with the current account.
Returns a string with the email associated with the current account.
Returns an object with the name, balance and first card associated with the current account. The advantage of this method is that it gets all of this information with a single GET request. The structure of the returned object is as follows: { name, balance, firstCard }.
Returns an object with all the received transactions. The individual transactions are returned as objects with the following structure: { date, phone, amount }.
Returns an object with all the sent transactions. The individual transactions are returned as objects with the following structure: { date, phone, amount }.
Returns a string with the name of the first card.
Return an object with the name, hash and balance of the main card. The object structure is as follows: { name, hash, balance }.
Returns an object with all the available cards in the account and their respective hashes. The individual cards are returned as objects with the following structure: { cardName, cardHash }.
Returns true if successful and false if something went wrong.
Required parameters:
-
phone: The number of the person to whom you want to send the money.
-
amount: The amount of money that you want to send.
Optional parameters:
-
message: The message that will be attached to the transaction. By default it is an empty string.
-
cardHash: This parameter is used to specify the card from which the transaction will be initiated. By default
cardHashis the same as the hash from the main card.
.fetchPage(route)
Will make a GET request to the given route/resource and return the response. The complete path will be: https://www.athmovil.com/web/ + route
.fetchMainPage()
Will make a GET request to https://www.athmovil.com/web/mainMenu.htm and return the response.
.postData(data, endpoint)
Will make a POST request with the given data to the specified endpoint and return the response. The complete path will be: https://www.athmovil.com/web/ + endpoint.
- More features
- Documentation
- Proper test suite
- Major refactoring
- Better error handling
- Support for multiple cards
Another interesting project is comming soon!
Copyright (c) 2019 Arnaldo Gabriel
This project is licensed under the MIT License.