URL routing inspired by express for the frontend!
Aviation helps you build simple javascript apps that run right in the browser. No server side processing needed.
Aviation automatically tracks link clicks, history events and page loads, and invokes your functions.
- Create dynamic websites (especially dashboards) easily.
- In-built response functions for stuff like changing content and setting cookies.
- Parses URLs, queries, cookies and parameters for you.
Getting Started
First include Aviation in your code
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/aviation"></script>Let's create a simple app that shows a welcome message on page load!
var app = Aviation()
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
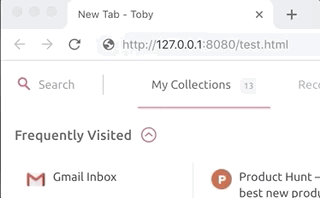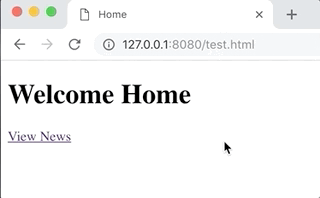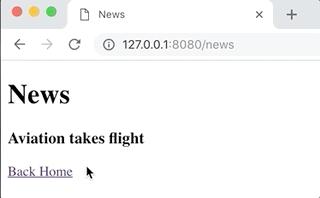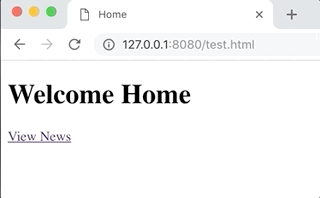
res.html("<h1>Welcome Home</h1>")
})Now, let's unleash Aviation's capabilities with a dynamic example.
In this example, we'll create a menu on page load.
We'll be able to browse to different pages, without actually reloading the page.
var app = Aviation()
app.on("/", function(req, res, next) {
res.page("Home").html("<h1>Welcome Home</h1> <a href='/news'>View News</a>")
})
app.on("/news", function(req, res, next) {
res.page("News").html("<h1>News</h1> <h3>Aviation takes flight</h3> <a href='/'>Back Home</a>'")
})Here's the result:
Functions
Aviation(options)
This creates a new instance of Aviation with the supplied options. Possible options are:
- contentWrapper - This is the element res.html() will update with content. Defaults to
body. - onError (Function) This is the function that will be called when an error occurs. It's provided with the err, req, res, next arguments. Defaults to
console.error. - caseSensitive - (Boolean) Should /app and /App not be considered the same? Defaults to false.
- strict - (Boolean) Should /app and /app/ not be considered the same? Defaults to false.
- removeFromPath - (String or Regex) Removes the string or matching regex from all paths. Useful for running local projects, or anything inside a directory.
- events - (Array of strings) The events to listen for. Defaults to
["click"]. - source - (String) The source types to listen for. Defaults to
a[href]:not([target='_blank']):not(.skip-aviation). - eventWrapper - The element that we listen to all events for. Defaults to
document. - changeURL - (Boolean) Whether the browser URL should be changed? This automatically sets itself to false if the web app was launched in a containerized state (file://). If the web app starts with in any other context (eg https:// for web), this defaults to false. Helps deal with Cordova & Electron.
- skipOnLoad - (Boolean) Should Aviation skip handling the URL on page load?
- loadEvents - (Array of strings) The event that Aviation listens for when the page is being loaded (This doesn't do anything if
skipOnLoadis set to true). The default is["DOMContentLoaded"]. You can also set this to["deviceready"]for Cordova (Although Cordova also fires the DOMContentLoaded event, so this is only if you want to use the Cordova plugins as soon as Aviation sends a request). - skipPopstate - (Boolean) Should Aviation skip listening to the browser for backward & forward buttons? Defaults to false.
Returns the .use() and .handle() functions.
.use(callback) or .use(path, callback)
This function registers a callback that Aviation will call when a request that matches its path is received. It also has an alias, .on(path, callback).
The path can be an array of paths, or a simple string, or a regex. When a path isn't supplied, all requests are routed to that callback.
Advanced Paths
You can specify parameters in the path. Aviation will expose these using req.params.
app.use("/users/:user/orders/:order", function(req) { console.log(req.params) })You can also specify wildcards. For example, Aviation will send a request for /users/dev/orders to the following function.
app.use("/users/*", function(req) { console.log(req.url) }).handle(url)
This function handles loading a new URL. It can also handle events. Advanced usages can directly call this when they want to use Aviation rather than waiting for someone to click a link.
Callback Functions
Whenever Aviation invokes a callback, it provides three functions as arguments.
function myCallback(request, response, next) {
}Request
- url - This is the URL of the request.
- hostname - This is the hostname (domain) of the request.
- path - This is the path of the request, like /app.
- protocol - This is the protocol of the request.
- secure - Boolean, whether the request is over HTTPS.
- query - Key-value object, this is the parsed query string of the URL.
- params - Key-value object, these are the parameters for URL requests.
- cookies - Key-value object, these are the parsed browser cookies.
- aviation - A reference to the Aviation instance.
Response
-
cookie(key, value, options) - Saves a cookie in the browser. Options can have:
maxAge,expires,path,domain,secureorsameSite.
-
clearCookie(key, options) - Deletes a cookie from the browser. Options other than
maxAgeandexpiresmust be the same or cookie deletion won't work.
-
redirect(url) - Redirects to this URL. If Aviation has a callback for this URL, it'll be called, else a real redirection will occur. It also has an alias,
location(url).
- page(title, url) - Updates the page title and creates a history event. If no URL is specified, the request URL will be used.
- html(content) - Essentially a wrapper for jQuery's .html(). Updates the content of the page. It can also accept a reference or element created directly by jQuery like res.html($('').text("Example!"))
Next()
Invoking next() makes Aviation run the next matching function for this request.
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
//Some error occured, skip to next function.
next()
})
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
console.log("Running backup function")
})Aviation.element(type, [props], ...children)
Writing HTML as strings in JS is hard. So just write pure HTML, JSX helps you with that. And this function, when set as the pragma for JSX instead of React.createElement, turns that JSX into safe JS that can be used on any browser. Returns a jQuery element.
Using Aviation.element through JSX via Babel:
const jsxCode = 'var el = <div></div>; console.log(el)' //OR: fs.readFileSync("./app.jsx")
const babel = require("@babel/core")
var result = babel.transformSync(jsxCode, {presets: [["@babel/preset-react", {pragma: "Aviation.element"}]]})
//JS: result.codeUsing Aviation.element directly:
var el = Aviation.element("div", {class: "test-div"}, "text inside div")
console.log(el)