cdt2d
A robust 2D constrained Delaunay triangulation library written in JavaScript.
WORK IN PROGRESS
Demo
To test out this module, you can open up a demo in your browser with the following link:
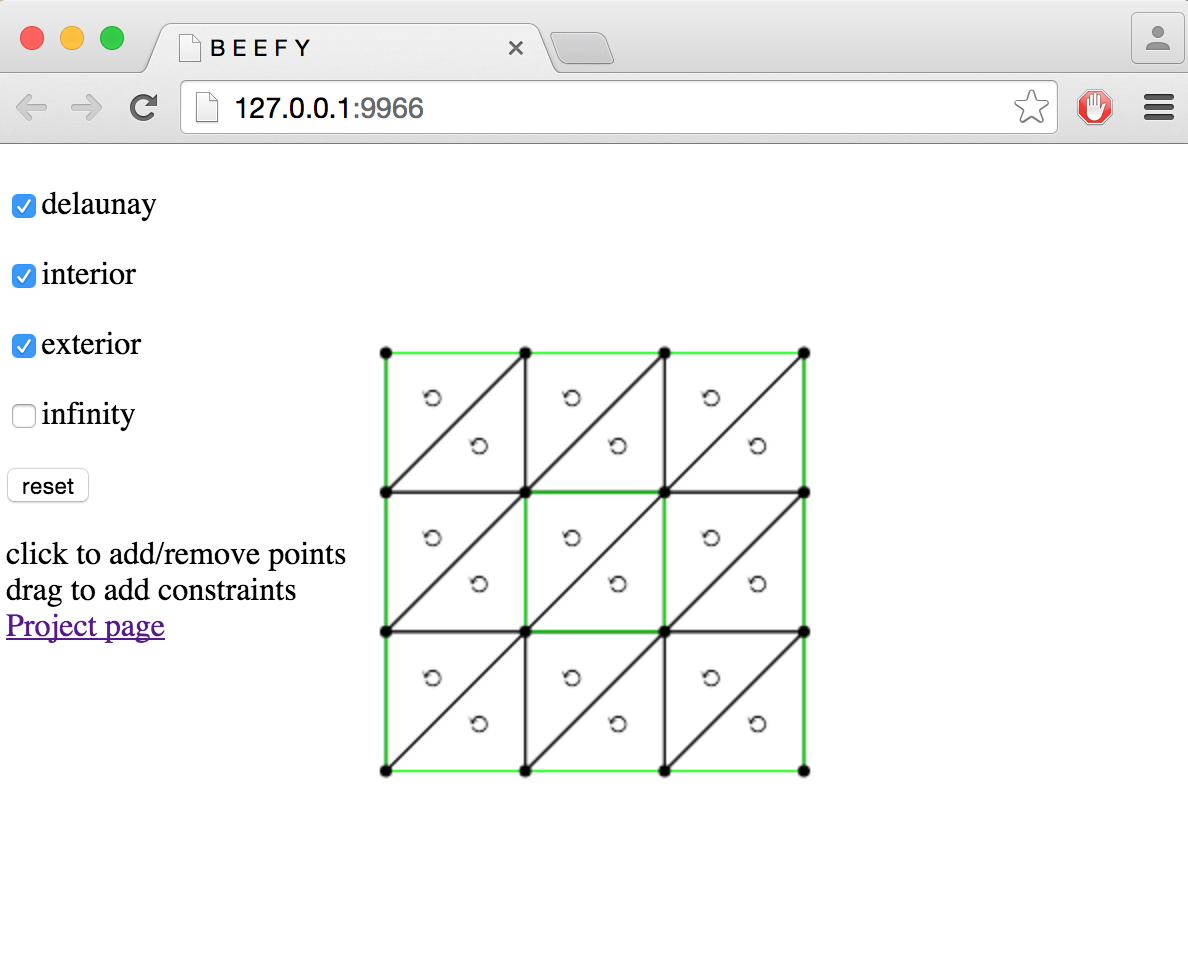
cdt2d demo
- Click to add points
- Click on a point to remove it
- Drag one point onto another to add an edge constraint
- Click on a green edge to remove a constraint
- Toggle options by clicking on the checkboxes on the left
- Click reset to clear all points
Examples
Simple example
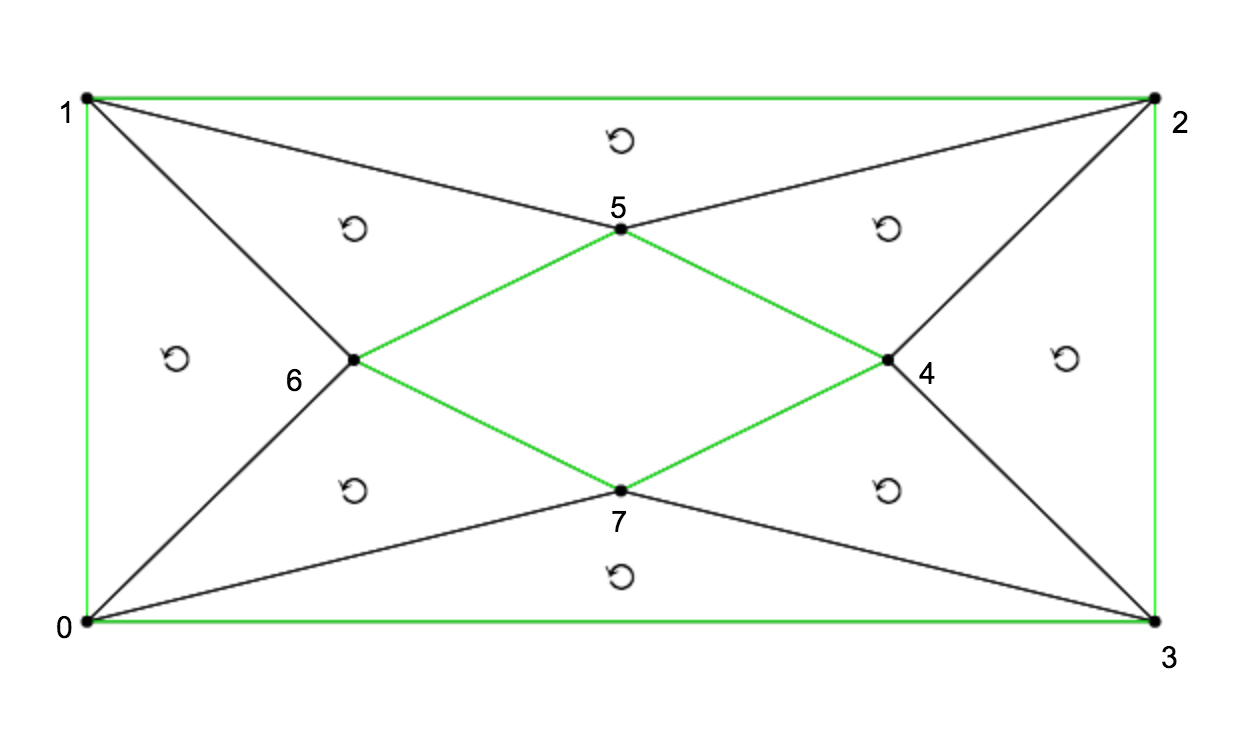
Here is a simple example showing how to invoke cdt2d:
//First we need to reqire the modulevar cdt2d = //Then we define a list of points, represented as pairs of x,y coordinatesvar points = -2-2 -2 2 2 2 2-2 1 0 0 1 -1 0 0-1 //Next we can optionally define some edge constraints// This set of edges determines a pair of loopsvar edges = //Outer loop 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 0 //Inner loop 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 4 //Finally we call cdt2d with the points and edges// The flag {exterior: false} tells it to remove exterior facesconsoleOutput
The above program will output the following triangles:
0 3 7 0 6 1 0 7 6 1 5 2 1 6 5 2 4 3 2 5 4 3 4 7 Each triangle is represented as an array of 3 indices of points. We can visualize this data in the following figure:
Messy graphs
If your input doesn't satisfy the validity invariants (ie no self intersections, duplicate vertices or t-junctions), then you will need to preprocess it to clean it up. One way to do this is with the clean-pslg module. Here is an example showing how to do this:
var cleanPSLG = var cdt2d = var points = -1 0 1 0 0-1 0 1 var edges = 0 1 1 2 //This updates points/edges so that they now form a valid PSLG //Generate the triangulationconsoleOutput
TODO
Polygon example
It is also pretty easy to use this module with polygons, as one would get from a GeoJSON file. To do this, it is first necessary to convert them into a planar straight line graph. This can be done using the poly-to-pslg module:
var toPSLG = var cdt2d = TODO
Polygon with holes example
The above procedure even works if the polygons have holes:
var toPSLG = var cdt2d = TODO
Delaunay triangulation
You can also use cdt2d to generate Delaunay triangulations of arbitrary point sets in the plane:
TODO
Install
This module works in any modern CommonJS environment. You can install it using npm with the following command:
npm i cdt2d
You should be able to then use it in node or on the web with browserify.
API
var cells = require('cdt2d')(points[, edges, options])
Constructs a constrained Delaunay triangulation of a planar straight-line graph.
pointsare the vertices of the triangulation, represented by pairs of numbers.edgesis an optional list of edge constraints which must occur within the triangulation. These constraints are given by pairs of indices of points. If not specified, then no constraints are used.optionsis an object which takes some optional parameters.delaunayif this flag is set to true, then the resulting triangulation is converted to a Delaunay triangulation by edge flipping. Otherwise if it is false, then an arbitrary triangulation is returned. (Defaulttrue)interiorif set, only return interior faces. See note. (Defaulttrue)exteriorif set, only return exterior faces. See note. (Defaulttrue)infinityif set, then the triangulation is augmented with a point at infinity represented by the index-1. (Defaultfalse)
Returns A list of all triangles represented as triples of indices of vertices
Note on interior/exterior classification Interior/exterior faces are classified by treating the constraint edges as the boundary and traversing the triangulation. The point at infinity is in the exterior of the set, and other faces are classified by the parity of the path with fewest crossings from the face to the point at infinity.
Assumptions This module makes the following assumptions about the points and edge constraints:
- No point in the input is duplicated
- No pair of edge constraints cross in their relative interior
- No point is contained in the relative interior of an edge (ie no T-junctions)
If your input does not satisfy these conditions, you will need to preprocess it first (using clean-pslg for example) otherwise cdt2d may return incorrect results.
Limitations Currently there is no way to specify that only some edge constraints are to be included in the boundary. It is also not possible to add a constraint from a vertex to the point at infinity. If there is enough demand I may add these features or perhaps create a separate module.
Benchmarks and comparisons
Assertion: cdt2d is the only non-broken triangulation library in JavaScript.
- TODO Catalogue failing cases for other libraries
- TODO Need to measure performance and finetune
Libraries to compare against:
earcutpoly2tripnltrilibtess.js
License
(c) 2015 Mikola Lysenko. MIT License