Fireshell
A shell for firebase realtime database and cloud firestore.
Fireshell is a CLI tool which can be used to execute realtime database and cloud firestore queries in your terminal.
Changelog v1.2.0
Release Highlights
- Added commands for setting and resetting config file.
- Added command for running multiple queries at once by taking input from a file.
Installation
To install fireshell, simply pull up your terminal and run the following command :-
npm install -g fireshell
NOTE: You need to have Node.js and Node Package Manager installed in order to install fireshell.
Running the shell
Connecting the shell with the database
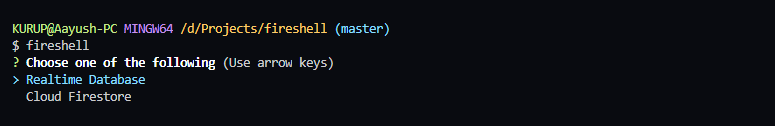
To start the shell, simply run fireshell in your terminal. You will be prompted a few questions. These questions will be prompted the only the first you run the shell or when you reset the shell. The answers provided for these questions will be used for creating a config.json file.
First you'll have to choose the service you want to connect with :-
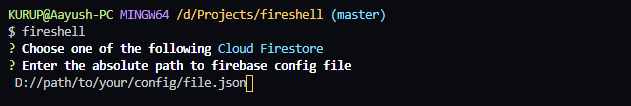
Then you have to provide the absolute path to your firebase config file. It has to be a JSON file that you get from firebase to connect your application with your firebase project.
Important Note:- Please make sure that the firebase config file has a key called "projectId". This key is very important in order to authenticate. If your config file has a key called "project_id", rename it to "projectId".
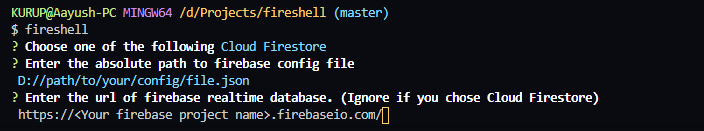
The last prompt will ask you to enter the reltime database url. If you chose firestore in the 1st prompt, then your can ignore this question. Otherwise, enter the url.
Note:- In versions >= 1.1.0 these prompts will be asked only once. After that, the shell will connect automatically using previously provided parameters.
Writing Queries
Your queries must start with the keyword db. This db is a variable that stores reference to the database object. You can chain the rest of your query as you normally do.
For realtime database, make sure that you end any read query or any query that returns some data with the once method and pass value as its argument.
Examples of realtime database queries
// Create operation
> db.ref().child('user').set({name: "Iron Man", "alter-ego": "Tony Stark"})
// Read operation
> db.ref().child('user').once('value')
// Update operation
> db.ref().child('user').update({name: "Batman", "alter-ego": "Bruce Wayne"})
// Delete operation
> db.ref().child('user').remove()
Examples of cloud firestore queries
// Create operation
> db.collection('user').add({name: "Spiderman", "alter-ego": "Peter Parker"})
// Read operation
> db.collection('user').get()
// Update operation
> db.collection('user').doc('some-id').update({name: "Flash", "alter-ego": "Barry Allen"})
// Delete operation
> db.collection('user').doc('some-id').delete()
For more help, check out Cloud Firestore and Realtime Database docs.
Running the CLI commands
There are 3 CLI commands that you can run :-
- set-config :- Used to set the config parameters.
fireshell set-config <absolute path to firebase config file> <database type>
This command requires you to pass 2 additional arguments - absolute path to the firebase config json file and the database type. Database type will only take 'database' or 'firestore'. Additionally, if you are using realtime database, you need to pass the realtime database url as another optional argument as follows:-
fireshell set-config <absolute path to firebase config file> <database type> -u <realtime database url>
- reset :- Used to reset the config file.
fireshell reset
When you run this command, the previously provided config is deleted and you need to provide the config parameters again.
- firerun :- Used to run multiple database queries from a file and return output in a file.
fireshell firerun <input filepath> <output filepath>
You have to pass the path to input file and path to output file as arguments. Refer sample.txt to understand how to format the input file.
Contributors
Made with contributors-img.