Github deploy status
Node.js scripts that update a Github repository's deployment status.
Did you know that you keep track of your deployments right on Github.com? You can do this through the Environment tab!
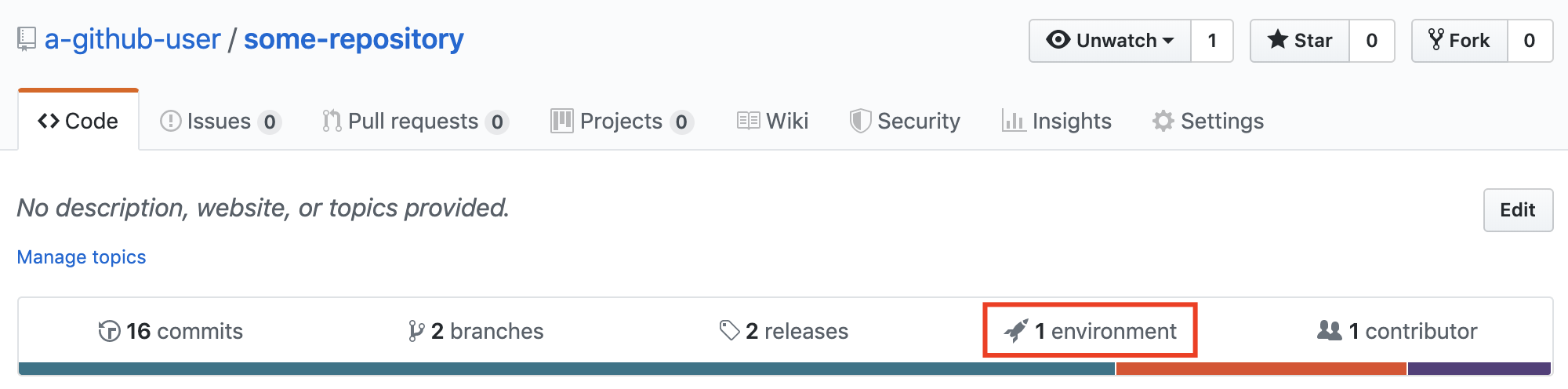
What is the Environment tab and why don't I see it on my repositories?
The Environment tab only shows up if you add a deployment to your Github repository. Once you've added a deployment, you can update its status to show whether it's pending, in progress, successful, failed, or errored. Some third-party integrations such Heroku do this for you, so when you deploy through that service, it shows up on your Github page. If you deploy through custom CI scripts using services such as Travis CI, this won't show up automatically.
This package provides CLI scripts to help interface with Github's deployments API so you can track your deployments right in your pull requests:
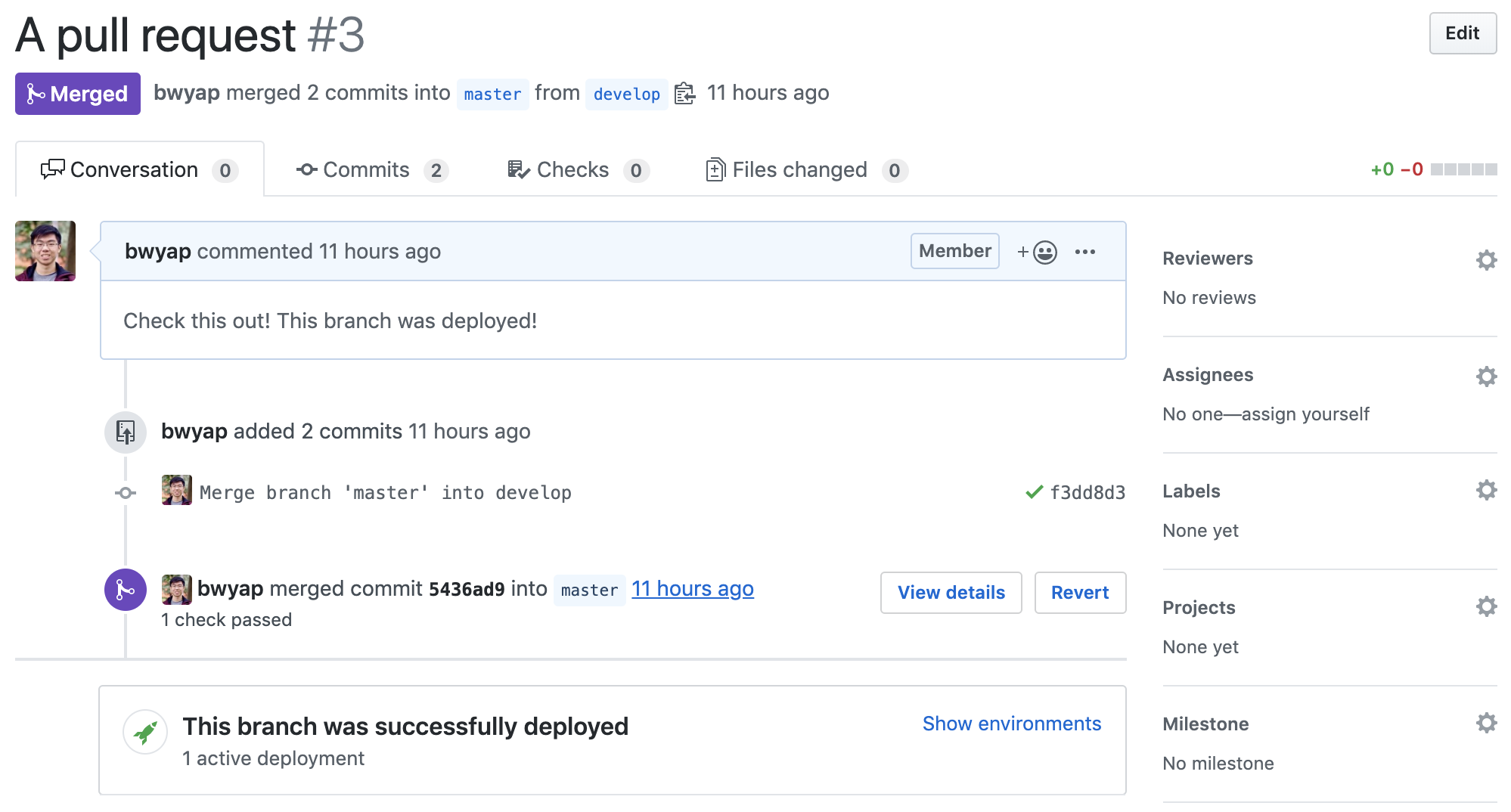
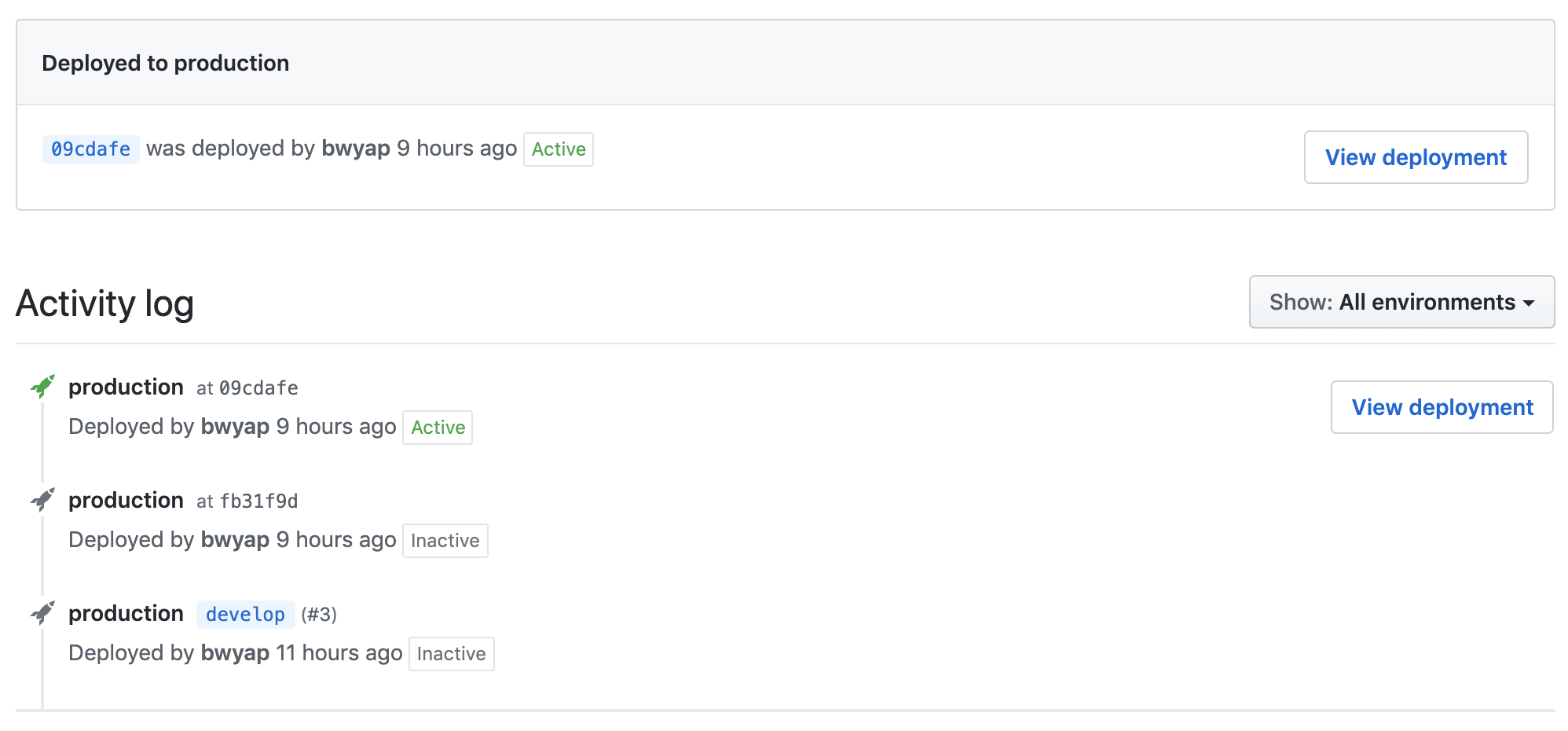
And see a history of your deployments in the Environment tab!
Usage
Install this package using yarn or npm:
yarn add -D github-deploy-statusnpm i -D github-deploy-statusYou can now use the command right in your shell!
github-deploy-status ...Just make sure you give the correct arguments. See below for the arguments required.
Arguments
--token <token>
This argument is required.
Interfacing with the Github API requires authentication. Create a
personal API token
and provide it to the script so that it can use it to authorise your
requests. Ensure that you grant your token the repo_deployment scope.
--action <action> or -a <action>
This argument is required.
<action> must be one of the following values:
createfail_if_unsuccessfulsuccessfailureerror
Using create action will create a new deployment.
The fail_if_unsuccessful action is special - it will first check the status
of the latest deployment. If it is NOT successful (e.g. it is pending or in
progress), it will add a new failure status. This is useful to call at the end
of your deployment scripts in case the deployment doesn't complete and there is
no way to receive feedback other than to check the deployment status.
There must be an existing deployment before you add deployment statuses. The remaining actions (success, failure, error) will add the respective statuses to the most recent deployment.
--environment <environment> or -e <environment
This argument is required.
Use this to provide the name of the environment you are deploying to. Common
values for this are dev, staging or production.
--ref <ref> or -r <ref>
This argument is required.
Provide the ref of what you want to deploy from your repository. This can be a tag, branch, or SHA.
--user <username> or -u <username>
This argument is required.
Provide the username of the user who owns the repository that you are managing deployments for.
--repo <repo_name> or -p <repo_name>
This argument is required.
Provide the name of the repository that you are managing deployments for.
--url <url> or -l <url>
This argument is optional.
Provide a link to the deployed environment if you want the View deployment button to show up next to your active deployments.
Example
One way to take advantage of this script is to add it to your package.json and .travis.yml:
package.json:
.travis.yml:
... jobs: include: - stage: Staging before_deploy: - yarn add github-deploy-status - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a create -e staging -r develop - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a in_progress -e staging -r develop deploy: ... on: branch: develop after_deploy: - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a success -e staging -r develop -l https://staging.myapp.com - stage: Production before_deploy: - yarn add github-deploy-status - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a create -e production -r master - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a in_progress -e production -r master deploy: ... on: branch: master after_deploy: - yarn gds --token $GITHUB_TOKEN -a success -e production -r master -l https://myapp.com...In the above example, a deployment is created when Travis starts a deployment
(whose status is set to pending by default), and the status is set to success
once the deployment completes. The user's Github access token is stored as an
environment variable on Travis CI and is access through $GITHUB_TOKEN.