An Rspack plugin for generating HTML files.
This plugin is forked from jantimon/html-webpack-plugin, it is designed for Rspack and provides better performance than html-webpack-plugin.
The function of this plugin is basically the same as html-webpack-plugin.
Big thanks to
html-webpack-plugincreators and contributors for their great work. ❤️
Differences with html-webpack-plugin:
- Designed for Rspack
- Import type from
@rspack/core
- Import type from
- Less dependencies
- Removed
html-minifier-terserand allows to use any HTML minimizer - Removed
lodashdependency with a forked minimal version - Removed
pretty-errordependency - Removed
webpackpeer dependency
- Removed
- Performance improvements for Rspack:
- Removed support for HTML5 Application caches (it has been deprecated)
- Reuse
compilation.entrypoints
# npm
npm add -D html-rspack-plugin
# yarn
yarn add -D html-rspack-plugin
# pnpm
pnpm add -D html-rspack-pluginThe plugin will generate an HTML5 file for you that includes all your Rspack bundles in the head using script tags. Just add the plugin to your Rspack config as follows:
rspack.config.js
const HtmlRspackPlugin = require('html-rspack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: 'index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'index_bundle.js',
},
plugins: [new HtmlRspackPlugin()],
};This will generate a file dist/index.html containing the following
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Rspack App</title>
<script defer src="index_bundle.js"></script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>If you have multiple Rspack entry points, they will all be included with script tags in the generated HTML.
If you have any CSS assets in Rspack's output (for example, CSS extracted with the CssExtractRspackPlugin) then these will be included with <link> tags in the HTML head.
If you have plugins that make use of it, html-rspack-plugin should be ordered first before any of the integrated Plugins.
You can pass a hash of configuration options to html-rspack-plugin. Allowed values are as follows:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title |
{String} |
Rspack App |
The title to use for the generated HTML document |
filename |
{String|Function} |
'index.html' |
The file to write the HTML to. Defaults to index.html. You can specify a subdirectory here too (eg: assets/admin.html). The [name] placeholder will be replaced with the entry name. Can also be a function e.g. (entryName) => entryName + '.html'. |
template |
{String} |
`` | Rspack relative or absolute path to the template. By default it will use src/index.ejs if it exists. Please see the docs for details |
templateContent |
{string|Function|false} |
false | Can be used instead of template to provide an inline template - please read the Writing Your Own Templates section |
templateParameters |
{Boolean|Object|Function} |
false |
Allows to overwrite the parameters used in the template - see example |
inject |
{Boolean|String} |
true |
true || 'head' || 'body' || false Inject all assets into the given template or templateContent. When passing 'body' all javascript resources will be placed at the bottom of the body element. 'head' will place the scripts in the head element. Passing true will add it to the head/body depending on the scriptLoading option. Passing false will disable automatic injections. - see the inject:false example
|
publicPath |
{String|'auto'} |
'auto' |
The publicPath used for script and link tags |
scriptLoading |
{'blocking'|'defer'|'module'|'systemjs-module'} |
'defer' |
Modern browsers support non blocking javascript loading ('defer') to improve the page startup performance. Setting to 'module' adds attribute type="module". This also implies "defer", since modules are automatically deferred. |
favicon |
{String} |
`` | Adds the given favicon path to the output HTML |
meta |
{Object} |
{} |
Allows to inject meta-tags. E.g. meta: {viewport: 'width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no'}
|
base |
{Object|String|false} |
false |
Inject a base tag. E.g. base: "https://example.com/path/page.html
|
minify |
(html: string) => string | Promise<string> |
`` | A function to minify HTML, see minification below for more details. |
hash |
{Boolean} |
false |
If true then append a unique Rspack compilation hash to all included scripts and CSS files (i.e. main.js?hash=compilation_hash). This is useful for cache busting |
cache |
{Boolean} |
true |
Emit the file only if it was changed |
showErrors |
{Boolean} |
true |
Errors details will be written into the HTML page |
chunks |
{?} |
? |
Allows you to add only some chunks (e.g only the unit-test chunk) |
chunksSortMode |
{String|Function} |
auto |
Allows to control how chunks should be sorted before they are included to the HTML. Allowed values are 'none' | 'auto' | 'manual' | {Function}
|
excludeChunks |
{Array.<string>} |
`` | Allows you to skip some chunks (e.g don't add the unit-test chunk) |
xhtml |
{Boolean} |
false |
If true render the link tags as self-closing (XHTML compliant) |
Here's an example Rspack config illustrating how to use these options
rspack.config.js
{
entry: 'index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'index_bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
title: 'My App',
filename: 'assets/admin.html'
})
]
}To generate more than one HTML file, declare the plugin more than once in your plugins array
rspack.config.js
{
entry: 'index.js',
output: {
path: __dirname + '/dist',
filename: 'index_bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin(), // Generates default index.html
new HtmlRspackPlugin({ // Also generate a test.html
filename: 'test.html',
template: 'src/assets/test.html'
})
]
}If the default generated HTML doesn't meet your needs you can supply your own template. The easiest way is to use the template option and pass a custom HTML file. The html-rspack-plugin will automatically inject all necessary CSS, JS and favicon files into the markup.
Details of other template loaders are documented here.
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
title: 'Custom template',
// Load a custom template (lodash by default)
template: 'index.html',
}),
];index.html
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title><%= HtmlRspackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>If you already have a template loader, you can use it to parse the template. Please note that this will also happen if you specify the html-loader and use .html file as template.
rspack.config.js
module: {
loaders: [
{ test: /\.hbs$/, loader: "handlebars-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
title: 'Custom template using Handlebars',
template: 'index.hbs'
})
]You can use the lodash.template syntax out of the box. If the inject feature doesn't fit your needs and you want full control over the asset placement, you can write your own template.
The following variables are available in the template by default (you can extend them using the templateParameters option):
-
HtmlRspackPlugin: data specific to this plugin-
HtmlRspackPlugin.options: the options hash that was passed to the plugin. In addition to the options actually used by this plugin, you can use this hash to pass arbitrary data through to your template. -
HtmlRspackPlugin.tags: the preparedheadTagsandbodyTagsArray to render the<base>,<meta>,<script>and<link>tags. Can be used directly in templates and literals. For example:<html> <head> <%= HtmlRspackPlugin.tags.headTags %> </head> <body> <%= HtmlRspackPlugin.tags.bodyTags %> </body> </html>
-
HtmlRspackPlugin.files: direct access to the files used during the compilation.publicPath: string; js: string[]; css: string[]; favicon?: string;
-
-
webpackConfig: the Rspack configuration that was used for this compilation. This can be used, for example, to get thepublicPath(webpackConfig.output.publicPath). -
compilation: the Rspack compilation object. This can be used, for example, to get the contents of processed assets and inline them directly in the page, throughcompilation.assets[...].source()(see the inline template example).
The template can also be directly inlined directly into the options object.
templateContent does not allow to use Rspack loaders for your template and will not watch for template file changes
rspack.config.js
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
templateContent: `
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>
`,
});The templateContent can also access all templateParameters values.
templateContent does not allow to use Rspack loaders for your template and will not watch for template file changes
rspack.config.js
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
inject: false,
templateContent: ({ HtmlRspackPlugin }) => `
<html>
<head>
${HtmlRspackPlugin.tags.headTags}
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
${HtmlRspackPlugin.tags.bodyTags}
</body>
</html>
`,
});To include only certain chunks you can limit the chunks being used
rspack.config.js
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
chunks: ['app'],
}),
];It is also possible to exclude certain chunks by setting the excludeChunks option
rspack.config.js
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
excludeChunks: ['dev-helper'],
}),
];You can use any HTML mimizer to minify the output HTML:
const { minify } = require('html-minifier-terser');
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
minify: (html) =>
minify(html, {
// options
}),
}),
];If the meta option is set the html-rspack-plugin will inject meta tags.
For the default template the html-rspack-plugin will already provide a default for the viewport meta tag.
Please take a look at this well maintained list of almost all possible meta tags.
Most meta tags are configured by setting a name and a content attribute.
To add those use a key/value pair:
rspack.config.js
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
meta: {
viewport: 'width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no',
// Will generate: <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
'theme-color': '#4285f4',
// Will generate: <meta name="theme-color" content="#4285f4">
},
}),
];The http-equiv attribute is essentially used to simulate a HTTP response header.
This format is supported using an object notation which allows you to add any attribute:
rspack.config.js
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
meta: {
'Content-Security-Policy': {
'http-equiv': 'Content-Security-Policy',
content: 'default-src https:',
},
// Will generate: <meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src https:">
// Which equals to the following http header: `Content-Security-Policy: default-src https:`
'set-cookie': {
'http-equiv': 'set-cookie',
content: 'name=value; expires=date; path=url',
},
// Will generate: <meta http-equiv="set-cookie" content="value; expires=date; path=url">
// Which equals to the following http header: `set-cookie: value; expires=date; path=url`
},
}),
];When the base option is used, html-rspack-plugin will inject a base tag. By default, a base tag will not be injected.
The following two are identical and will both insert <base href="http://example.com/some/page.html">:
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
base: 'http://example.com/some/page.html',
});new HtmlRspackPlugin({
base: { href: 'http://example.com/some/page.html' },
});The target can be specified with the corresponding key:
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
base: {
href: 'http://example.com/some/page.html',
target: '_blank',
},
});which will inject the element <base href="http://example.com/some/page.html" target="_blank">.
For long term caching add contenthash to the filename.
Example:
plugins: [
new HtmlRspackPlugin({
filename: 'index.[contenthash].html',
}),
];contenthash is the hash of the content of the output file.
Refer Rspack's Template Strings for more details
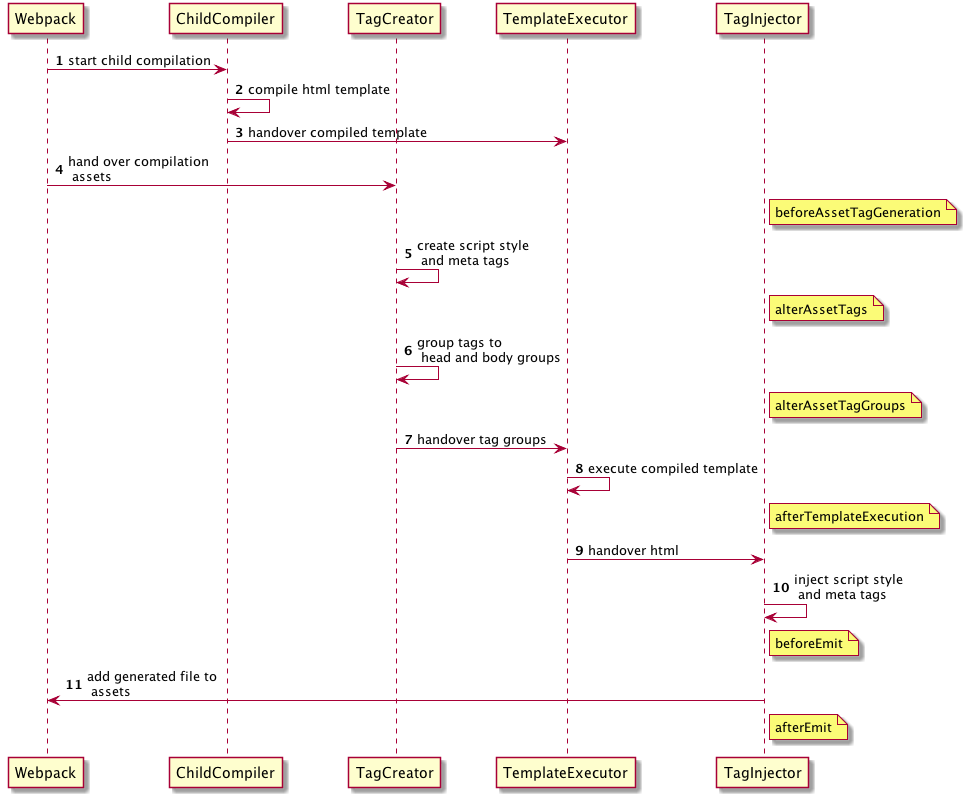
To allow other plugin to alter the HTML this plugin executes tapable hooks.
The lib/hooks.js contains all information about which values are passed.
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
assets: {
publicPath: string,
js: Array<{string}>,
css: Array<{string}>,
favicon?: string | undefined
},
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin
}>
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
assetTags: {
scripts: Array<HtmlTagObject>,
styles: Array<HtmlTagObject>,
meta: Array<HtmlTagObject>,
},
publicPath: string,
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin
}>
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
headTags: Array<HtmlTagObject | HtmlTagObject>,
bodyTags: Array<HtmlTagObject | HtmlTagObject>,
publicPath: string,
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin
}>
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
html: string,
headTags: Array<HtmlTagObject | HtmlTagObject>,
bodyTags: Array<HtmlTagObject | HtmlTagObject>,
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin,
}>
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
html: string,
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin,
}>
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook<{
outputName: string,
plugin: HtmlRspackPlugin
}>
Example implementation: webpack-subresource-integrity
plugin.js
const HtmlRspackPlugin = require('html-rspack-plugin');
class MyPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap('MyPlugin', (compilation) => {
console.log('The compiler is starting a new compilation...');
// Static Plugin interface |compilation |HOOK NAME | register listener
HtmlRspackPlugin.getCompilationHooks(compilation).beforeEmit.tapAsync(
'MyPlugin', // <-- Set a meaningful name here for stacktraces
(data, cb) => {
// Manipulate the content
data.html += 'The Magic Footer';
// Tell Rspack to move on
cb(null, data);
},
);
});
}
}
module.exports = MyPlugin;rspack.config.js
plugins: [new MyPlugin({ options: '' })];Note that the callback must be passed the HtmlRspackPluginData in order to pass this onto any other plugins listening on the same beforeEmit event
This project exists thanks to all the people who contribute.
You're free to contribute to this project by submitting issues and/or pull requests. This project is test-driven, so keep in mind that every change and new feature should be covered by tests.