ENGLISH | 日本語
A React component for rendering an interactive map of Japan, with customizable prefecture colors, hover effects, and tooltips.
- Display a map of Japan with all prefectures.
- Language support for Japanese and English prefecture names.
- Customize the colors of each prefecture.
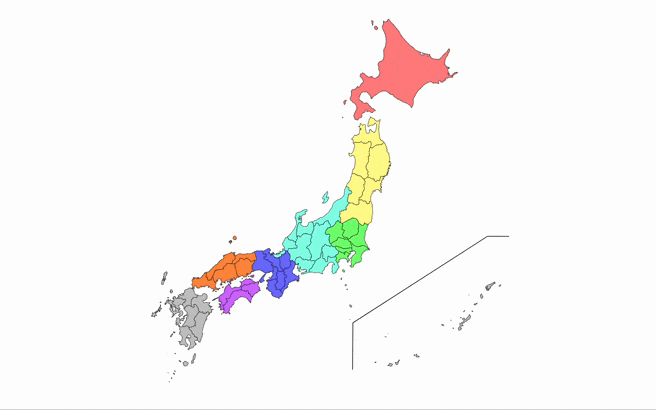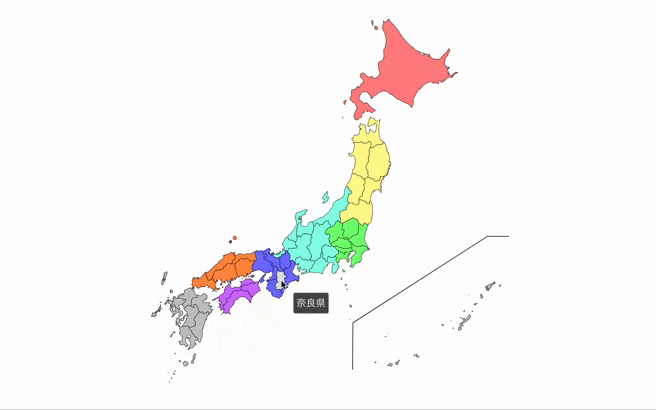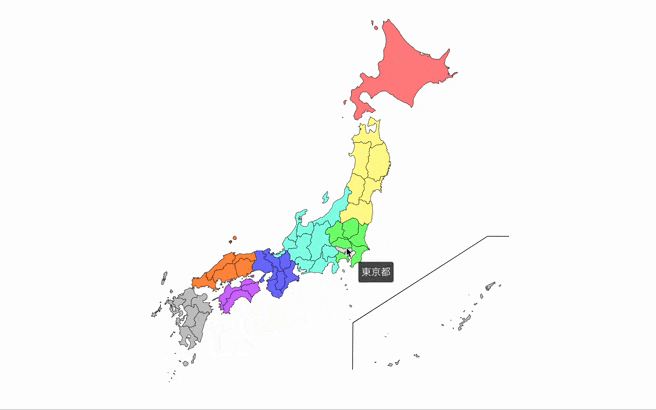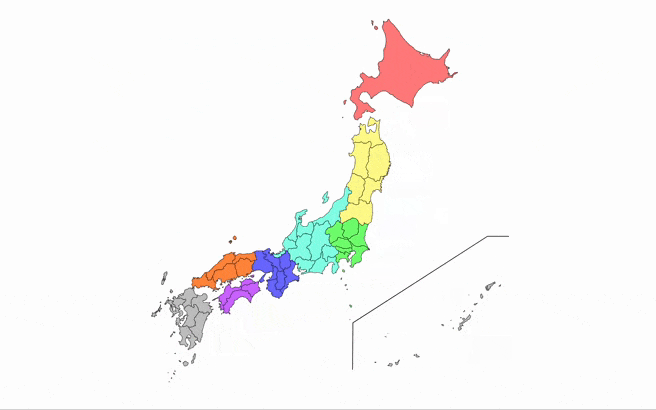
- Show tooltips with custom descriptions when hovering over prefectures.
- Supports dynamic data loading from JSON.
Install the library using npm:
npm install japanmapor...
pnpm
pnpm add japanmapyarn
yarn add japanmapbun
bun add japanmapImport the JapanMap component and use it in your React application:
import React from 'react';
import JapanMap from 'japanmap';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>Interactive Japan Map</h1>
<JapanMap
lang="en"
strokeColor="#000"
strokeWidth="0.5"
hoverColor="#E0E0E0"
bgColor="#f0f0f0"
size="600px"
/>
</div>
);
};
export default App;You can extend the default prefectures data by adding your own descriptions and fill colors with your own JSON file.
import React from 'react';
import JapanMap from 'japanmap';
import prefecturesData from './your/path/prefecturesdata.json';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>Interactive Japan Map</h1>
<JapanMap
data={prefecturesData}
lang="en"
strokeColor="#000"
strokeWidth="0.5"
hoverColor="#E0E0E0"
bgColor="#f0f0f0"
size="600px"
/>
</div>
);
};
export default App;The JapanMap component accepts the following properties (all are optional):
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
data |
Array<{ id: string; description: string; fill: string }> |
Data for the prefectures, including ID, description, and fill color. |
strokeColor |
string |
Color of the prefecture borders. |
strokeWidth |
string |
Width of the prefecture borders. |
hoverColor |
string |
Fill color when hovering over a prefecture. |
bgColor |
string |
Background color of the map. |
size |
string |
Width of the map component. |
The data prop expects an array of objects with the following structure:
[
{
"id": "JP01",
"description": "Hokkaido is the northernmost prefecture of Japan.",
"fill": "#88C0D0"
},
{
"id": "JP02",
"description": "Aomori is known for its apple production.",
"fill": "#BF616A"
},
...
]- id: A unique identifier for each prefecture. Using the ISO 3166-2:JP standard. (JP01...JP47)
- description: A string that will be shown in the tooltip when hovering over the prefecture.
- fill: The default fill color for each prefecture.
Please select the corresponding IDs for each prefecture from the table below. These IDs will be used to add entries to the JSON file and will help you identify each prefecture for labeling or changing their colors on the interactive map.
| ID | Prefecture | ISO 3166-2:JP |
|---|---|---|
| JP01 | Hokkaido | JP-01 |
| JP02 | Aomori | JP-02 |
| JP03 | Iwate | JP-03 |
| JP04 | Miyagi | JP-04 |
| JP05 | Akita | JP-05 |
| JP06 | Yamagata | JP-06 |
| JP07 | Fukushima | JP-07 |
| JP08 | Ibaraki | JP-08 |
| JP09 | Tochigi | JP-09 |
| JP10 | Gunma | JP-10 |
| JP11 | Saitama | JP-11 |
| JP12 | Chiba | JP-12 |
| JP13 | Tokyo | JP-13 |
| JP14 | Kanagawa | JP-14 |
| JP15 | Niigata | JP-15 |
| JP16 | Toyama | JP-16 |
| JP17 | Ishikawa | JP-17 |
| JP18 | Fukui | JP-18 |
| JP19 | Yamanashi | JP-19 |
| JP20 | Nagano | JP-20 |
| JP21 | Gifu | JP-21 |
| JP22 | Shizuoka | JP-22 |
| JP23 | Aichi | JP-23 |
| JP24 | Mie | JP-24 |
| JP25 | Shiga | JP-25 |
| JP26 | Kyoto | JP-26 |
| JP27 | Osaka | JP-27 |
| JP28 | Hyogo | JP-28 |
| JP29 | Nara | JP-29 |
| JP30 | Wakayama | JP-30 |
| JP31 | Tottori | JP-31 |
| JP32 | Shimane | JP-32 |
| JP33 | Okayama | JP-33 |
| JP34 | Hiroshima | JP-34 |
| JP35 | Yamaguchi | JP-35 |
| JP36 | Tokushima | JP-36 |
| JP37 | Kagawa | JP-37 |
| JP38 | Ehime | JP-38 |
| JP39 | Kochi | JP-39 |
| JP40 | Fukuoka | JP-40 |
| JP41 | Saga | JP-41 |
| JP42 | Nagasaki | JP-42 |
| JP43 | Kumamoto | JP-43 |
| JP44 | Oita | JP-44 |
| JP45 | Miyazaki | JP-45 |
| JP46 | Kagoshima | JP-46 |
| JP47 | Okinawa | JP-47 |
To build and run the project locally:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/daikiejp/japanmap.git
cd japanmap- Install dependencies:
npm install- Start the development server:
npm run devContributions are welcome! Please follow these steps:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch (git checkout -b feature/your-feature).
- Commit your changes (git commit -m 'Add a new feature').
- Push to the branch (git push origin feature/your-feature).
- Create a pull request.
👤 Danny Davila
- Website: https://daikie.jp
- X (formely Twitter): @daikiejp
- Github: @daikiejp
- Map data sourced from Simple Maps.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.