React Hook Dragula
Lightweight, strongly typed package with almost no dependencies. It uses
Dragula and React Hooks to smoothly manage the DOM state. It also adds a
context store which allows you to pass the data back and forth between
Dragula and React. take a look at the example project or the live
demo of the example project.
Install
yarn add react-hook-dragula
Usage
Initializing
// Typing for data which will be attached to dragula events. Yours will be different.
type Fruit = {
itemId: number;
itemName: string;
}
type DraggableStore = {
fruit: Fruit;
fruits: Fruit[];
setFruits: Dispatch<SetStateAction<Fruit[]>>;
}
const {
Dragula,
DragulaContainer,
Draggable,
DragulaHandle,
useDraggableStore,
useInternalStore,
useDrake,
} = initializeDragula<DraggableStore>();Basic dragging
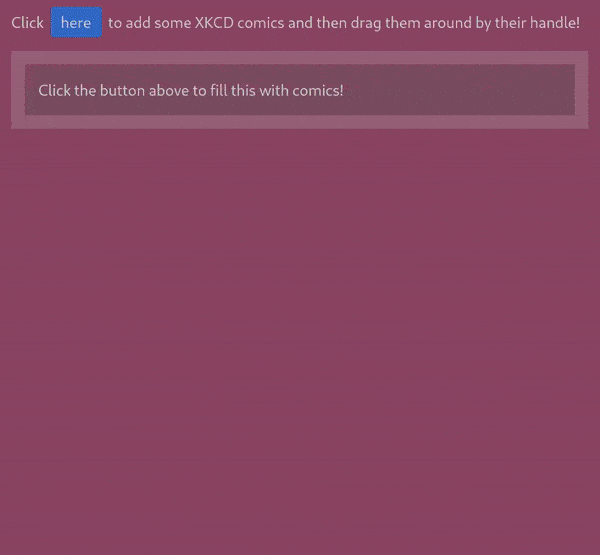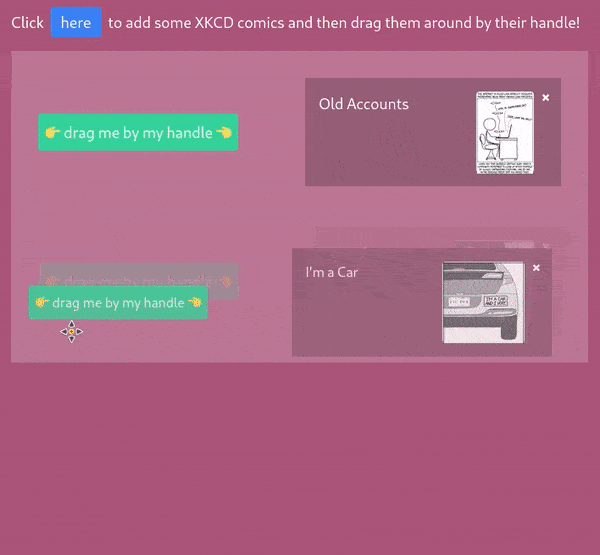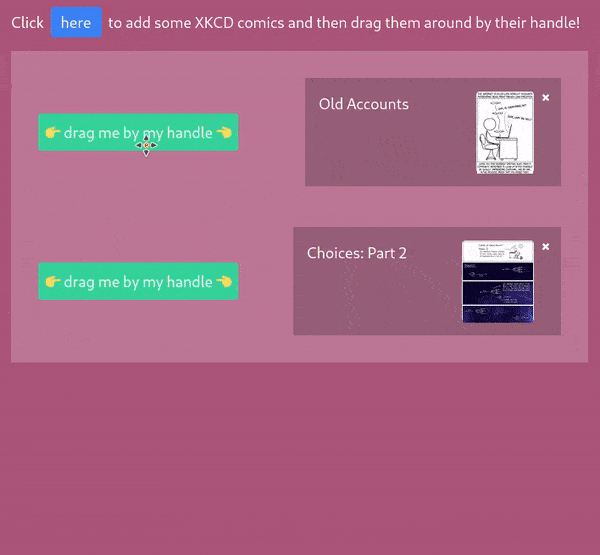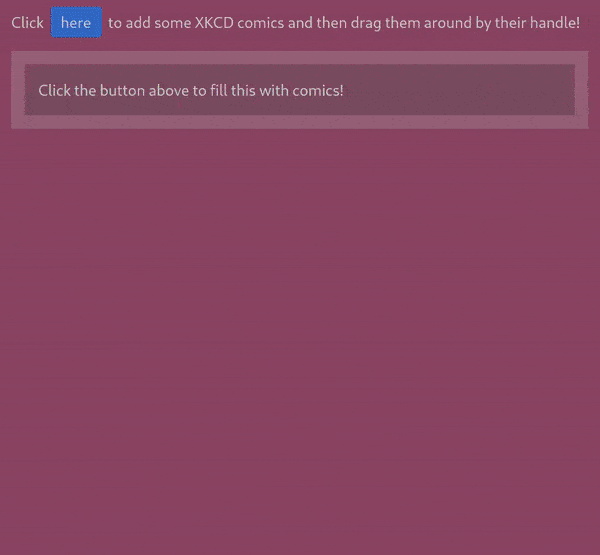
<Dragula>
<DragulaContainer>
<Draggable>
You can move these elements between these two containers
</Draggable>
</DragulaContainer>
<DragulaContainer>
<Draggable>
There's also the possibility of moving elements around in the
same container, changing their position
</Draggable>
</DragulaContainer>
</Dragula>Customizing Dragula options
<Dragula
options={{ moves: ({ container }) => !!container?.children.length > 1 }}
onDrop={() => console.log('dragula drop event!')}
>
<DragulaContainer>
<Draggable>
You can move these elements between these two containers
</Draggable>
<Draggable>
There's also the possibility of moving elements around in the
same container, changing their position
</Draggable>
<Draggable>
Anyting can be moved around. That includes images, links, or any other
nested elements.
</Draggable>
</DragulaContainer>
<DragulaContainer>
<Draggable>
This element can't be moved until a second one is added into it's container
</Draggable>
</DragulaContainer>
</Dragula>Attaching data to Dragula store
const [fruits, setFruits] = useState<Fruit[]>([
{ itemId: 1, itemName: 'apples' },
{ itemId: 2, itemName: 'oranges' },
{ itemId: 3, itemName: 'tomatoes' },
]);
<Dragula
onDrop={({ el, source }) => {
setFruits([...source.children].map(
({ draggableStore: { fruit } }) => draggableStore,
))
console.log('Dragual drop event for: ', el.draggableStore.fruit.itemName)
}}
>
<DragulaContainer>
{fruits.map(fruit => (
<Draggable
key={fruit.id}
draggableStore={{
fruit,
fruits,
setFruits,
}}
>
<div>{fruit.itemName} - id: {fruit.id}</div>
</Draggable>
))}
</DragulaContainer>
</Dragula>Using Drake and InternalStore
<Dragula
options={{ moves: ({ el }) => !!el?.internalStore.isMouseOverHandle }}
>
<DragulaContainer>
<Draggable>
<DragulaHandle>You can only drag this item by clicking on me!</DragulaHandle>
<div>You can move these elements between these two containers</div>
</Draggable>
<Draggable>
This item doesn't have a handle.. so it can't be moved at all!
</Draggable>
</DragulaContainer>
</Dragula>API
Extended typings
Each <Draggable/> node has a draggableStore and an internalStore object attached to it:
type InternalStore = {
isMouseOverHandle: boolean;
};
type DraggableStore<T> = T;
type ExtendedDrakeElement<T> = Element & {
draggableStore: DraggableStore<T>;
internalStore: InternalStore;
};
type ExtendedDrakeSource<T> = Element & { children: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>[] };Exported function
initializeDragula - - - returns object with entries:
Dragula: (props: DragulaContainerProps<T>) => <Dragula<T> {...props} />DragulaContainer: (props: HTMLProps<HTMLDivElement>) => (<DragulaContainer {...props} />)Draggable: (props: DraggableProps<T>) => <Draggable<T> {...props} />DragulaHandle: (props: DragulaHandleProps) => <DragulaHandle {...props} />useDraggableStore: () => useDraggableStore<T>()useInternalStore: () => useInternalStore()useDrake: () => useDrake()Component props
For the following, we have typings:
OnEventProps<T = typeof DraggableStore> {
clone: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>,
container: Element,
el: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>,
original: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>,
sibling: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>,
source: ExtendedDrakeSource<T>,
target: ExtendedDrakeElement<T>,
type: 'mirror' | 'copy',
}<Dragula
options={{
isContainer: ({ el }) => false,
moves: ({ el, source, handle, sibling }) => true,
accepts: ({ el, target, source, sibling }) => true,
invalid: ({ el, handle }) => true,
direction: "vertical",
copy: false,
copySortSource: false,
revertOnSpill: false,
removeOnSpill: false,
mirrorContainer: document.body,
ignoreInputTextSelection: true,
slideFactorX: 0,
slideFactorY: 0,
}}
onDrag={({ el, source }) => {}}
onDragEnd={({ el }) => {}}
onDrop={({ el, target, source, sibling }) => {}}
onCancel={({ el, container, source }) => {}}
onRemove={({ el, container, source }) => {}}
onShadow={({ el, container, source }) => {}}
onOver={({ el, container, source }) => {}}
onOut={({ el, container, source }) => {}}
onCloned={({ clone, original, type }) => {}}
dependencyList={[]}
/>See Dragula configuration for more info
<DragulaContainer {...props} />-
HTMLProps<HTMLDivElement>optional- This component has no special props
- Anything passed to it will be forwarded to a
<div />element
<Draggable
draggableStore={{}}
{...props}
/>-
draggableStoreObject, required- Type of store must match
<T>from when you initializedconst { Draggable } = initializeDragula<T>()
- Type of store must match
-
HTMLProps<HTMLDivElement>optional- Anything else passed to it will be forwarded to a
<div />element
- Anything else passed to it will be forwarded to a
<DragulaHandle {...props} />-
HTMLProps<HTMLDivElement>optional- This component has no special props
- Anything passed to it will be forwarded to a
<div />element
Custom Hooks
useDraggableStore: () => typeof DraggableStore<T> useInternalStore: () => { isMouseOverHandle: boolean; } // If Drake type & arrow functions were generic, then it would be this:
// useDrake: <T>() => Drake<ExtendedDrakeElement<T>>;
// Since they're not generic, we wind up with:
useDrake: () => ReturnType<ExtendedDragula<any>>;Acknowledgements
- Big thanks to all the work that Nicolás Bevacqua has done to build and maintain
Dragula!