-
Intializing the Sologenic XRPL stream with a hash-based queue
-
Intializing the Sologenic XRPL stream with a redis-based queue
-
Sending a Payment with the LedgerDeviceSigner as SigningMechanism
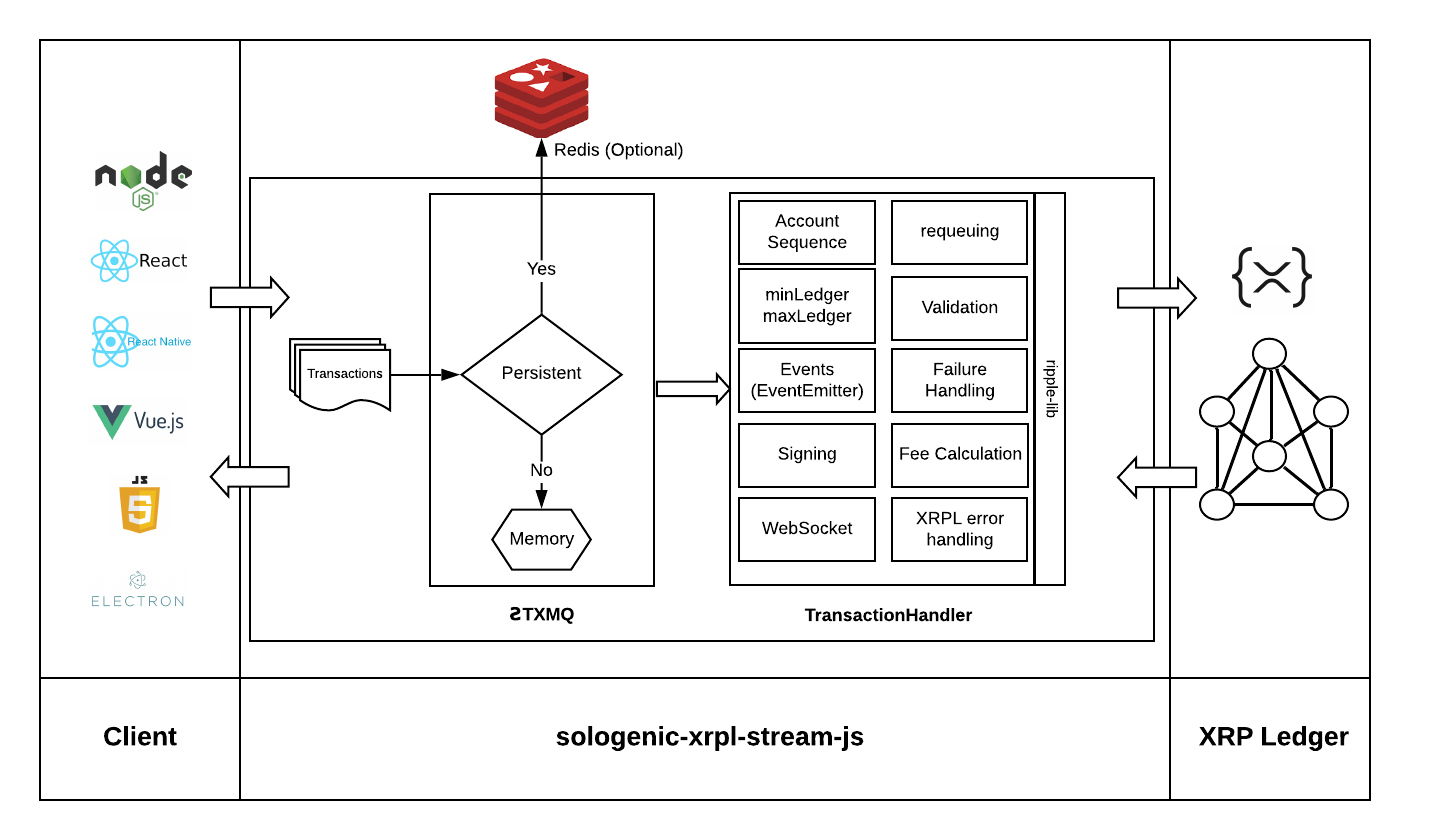
The sologenic-xrpl-stream-js enables clients to communicate and submit transactions to the XRP Ledger seamlessly and reliably.
This library provides reliable transaction handling following the guide provided by XRPL.org reliable transaction submissions.
Once a transaction is submitted, it is queued either using a Hash-based in-memory queue (non-persistent, ideal for front-end) or a Redis (persistent, ideal for backend). Transactions are queued and dispatched in sequence. Account sequence numbers, ledgerVersions and fees are also handled for each transaction that is being dispatched.
Events are reported back to the client using a global EventEmitter and transaction-specific EventEmitter. This allows clients to track the statuses of their transactions and take actions based on the results.
Production uses
-
SOLO ReactNative Wallet
-
SOLO React Electron Wallet
In general, there are two types of users who would benefit from using this library:
- Exchanges or users with large volumes of transactions who want to ensure they receive reliable delivery and can receive event notifications throughout the transactions validation process.
- Users who do not want to deal with transaction dispatching, validations and errors on the XRPL.
We have a community for questions and support at sologenic-dev.slack.com. To receive an invite for the community please fill out the form and we'll send you your invite link.
$ npm install sologenic-xrpl-stream-js
Each npm script defined in package.json can be run by simply running the command npm run-script <script name>
For example, notably the following scripts are frequently used when creating a packagable distribution, testing,
and generating documentation.
npm run-s build
The following command will iterate over all test cases (files with .spec.ts) as their suffix.
npm run-s test
The following command will iterate over all test cases (files with .spec.ts) as their suffix. But it will also watch for changes to the .spec.ts and .ts scripts and run tests on change.
npm run-s watch
The following command will generate both HTML and markdown documentation in the docs/ folder.
npm run-s doc
The following command will generate HTML only documentation.
npm run-s doc:html
The following command will generate markdown only documentation.
npm run-s doc:markdown
When using the sologenic-xrpl-stream-js library on the server side, we recommend using redis as the queue storage mechanism, whereas when using the library on the client side, we recommend using hash as on the client side you will most likely not have a redis server accessible to you.
The offline signing mechanism uses the standard sign() method included within the ripple-lib library. In previous versions of the library, ripple-lib signing was the only supported mechanism.
'use strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis (see SologenicOptions in documentation)
{
// Clear the cache before accessing the queue, since this is a hash-based
// queue it will be initialized empty, so this will have no effect.
clearCache: true,
queueType: "hash",
hash: {}
}
).connect()
}
)();'use strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis
{
// Clear the cache before accessing the queue, since this is a redis-based
// queue it will be emptied before after connecting. Please make sure there
// is no data in the database you're accessing you want to preserve.
clearCache: true,
queueType: 'redis',
redis: {
// The IP address or hostname of the redis queue
// host: '127.0.0.1',
// The port of the redis queue
// port: 6379,
// The password to access the redis queue
// password: 'password',
// The database number of the redis queue (if multiple database support is active)
// database: 1
}
}).connect();
}
);Note: When using a redis queue, you must have an active redis server which the transactional handler can connect.
The LedgerDevice signing mechanism implements the feature to sign transactions with a Ledger Nano S or Nano X. The LedgerDeviceSigner is initialized by passing a signingMechanism parameter to the SologenicTxHandler constructor. As with the other SigningMechanism on Sologenic XRPL stream, the library will handle all the signing process.
The initialization of this SigningMechanism HAS to be triggered by the user, otherwise the library will throw an exception.
Set SigningMechanism AFTER SologenicTxHandler initialization.
'use-strict';
import * as s from 'sologenic-xrpl-stream-js';
// First, initialize the SologenicTxHandler
async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com' // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis (see SologenicOptions in documentation)
{
// Clear the cache before accessing the queue, since this is a hash-based
// queue it will be initialized empty, so this will have no effect.
clearCache: true,
queueType: 'hash',
hash: {}
}
).connect();
}
};
// On User Action (i.e. click, keypress, etc) call for the establishConnection method.
// IMPORTANT: This method HAS to be called on User interaction, otherwise, the LedgerDevice communication library will throw an exception.
establishConnection().then(async () => {
// Set the Communication Object as the SigningMechanism.
await sologenic.setSigningMechanism(
new s.LedgerDeviceSigner({
ripple_server: RIPPLE_SERVER_WEBSOCKET // `i.e.: wss://s1.ripple.com/
})
);
// At the moment of connection, Ledger Devices return an array of accounts. This accounts are always going to be all the active accounts plus 1 inactive.
const { accounts } = await sologenic.connectSigner();
});The D'CENT Wallet signing mechanism implements the feature to sign transactions with a D'CENT wallet. The DcentSigner is initialized by passing a signingMechanism parameter to the SologenicTxHandler after initialization. As with the other SigningMechanism on Sologenic XRPL stream, the library will handle all the signing process/requests.
The initialization of this SigningMechanism HAS to be triggered by the user. Here are the steps:
'use-strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: "hash",
hash: {}
}
)
}
}).connect();
// On User Action (i.e. click, keypress, etc) call for a method to handle the connection. As follows:
const establishConnection = () => {
try {
// Set DcentSigner as Signing Mechanism
await sologenic.setSigningMechanism(new ƨ.DcentSigner());
// Trigger connection attempt
// At this point, the Dcent library will open a new tab to start connection.
// The user must have program installed called DCENT Bridge.
// The new tab will prompt the user with the request to install it.
// If address exists, then the connection has been successful.
const { address } = await sologenic.connectSigner();
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
}
}The SOLO Wallet signing mechanism implements the feature to sign transactions with a SOLO Wallet. (Available for Android and iOS). The SOLO Wallet signer is initialized by passing a signingMechanism parameter to the SologenicTxHandler after initialization. As with the other SigningMechanism on Sologenic XRPL Stream, the library will handle the signing process/requests.
new ƨ.SoloWalletSigner({
// This is the server that will handle the signing requests with the Wallet.
server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/', // REQUIRED
// HTML element where the QR Code to Sign in and establish connection with the wallet
// will be prompt.
container_id: HTML_ELEMENT_ID, // REQUIRED
// HTML element where the QR Code to sign a transaction will be shown as fallback
// in case the SOLO Wallet didn't receive the notification.
fallback_container_id: HTML_ELEMENT_ID, // REQUIRED
// Link to enable deeplinking to the SOLO WALLET when the webapp is being open in a mobile browser
deeplink_url: DEEPLINK_URL, // OPTIONAL
// Works together with deeplink_url. Both are needed in order for deeplinking to work, but not required
// for the signing to work
is_mobile: true || false // OPTIONAL
});The initialization of this SigningMechanism HAS to be triggered by the user. Here are the steps:
'use-strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: 'hash',
hash: {},
}
)
}
}).connect();
// On User Action (i.e click, keypress, etc) call for a method to show SignIn QR Code.
const establishConnection = () => {
// Set SoloWalletSigner as SigningMechanism
await sologenic.setSigningMechanism(
new ƨ.SoloWalletSigner({
server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/',
container_id: 'container_id',
fallback_container_id: 'fallback_container_id',
})
);
// In this moment, the Sologenic XRPL should prompt the SignIn QR Code on the element
// declared on the constructor. Then, user must scan this QR Code with their SOLO Wallet
// and sign the "transaction". After the transaction is signed. SOLO Wallet will send back
// the connection confirmation to the library as well as the address. Therefore, if the
// address exists, connection can be considered successful.
const { address } = await sologenic.connectSigner();
}The XUMM Wallet signing mechanim implements the feature to sign transactions with a XUMM Wallet. The XUMM Wallet signer is initialized by passing a signingMechanism parameter to the SologenicTxHandler after initialization. As with the other SigningMechanism on Sologenic XRPL Stream, the library will handle the signing process/requests.
This SigningMechanism requires the next arguments to be passed on its constructor.
new ƨ.XummWalletSigner({
// This is the server that will handle the signing requests with the Wallet.
server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/', // REQUIRED
// HTML element where the QR Code to Sign in and establish connection with the wallet
// will be prompt.
container_id: HTML_ELEMENT_ID, // REQUIRED
// HTML element where the QR Code to sign a transaction will be shown as fallback
// in case the XUMM Wallet didn't receive the notification.
fallback_container_id: HTML_ELEMENT_ID, // REQUIRED
// This property determines if the deeplinking feature will be enabled if the webapp is being accessed
// by a mobile browser. If you don't want to have this feature at all, just ignore this property.
is_mobile: true || false // OPTIONAL
});The initialization of this SigningMechanism HAS to be triggered by the user. Here are the steps:
'use-strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: 'hash',
hash: {},
}
)
}
}).connect();
// On User Action (i.e click, keypress, etc) call for a method to show SignIn QR Code.
const establishConnection = () => {
// Set XummWalletSigner as SigningMechanism
await sologenic.setSigningMechanism(
new ƨ.XummWalletSigner({
server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/',
container_id: 'container_id',
fallback_container_id: 'fallback_container_id'
})
);
// In this moment, the Sologenic XRPL should prompt the SignIn QR Code on the element
// declared on the contructor. Then, user must scan this QR Code with their SOLO Wallet
// and sign the "transaction". After the transaction is signed. XUMM Wallet will send back
// the connection confirmation to the library as well as the address. Therefore, if the
// address exists, connection can be considered successful.
const { address } = await sologenic.connectSigner();
}'use strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: "hash",
hash: {}
}
)
}
).connect();
// On User Action (i.e. click, keypress, etc) call for the establishConnection method.
// IMPORTANT: This method HAS to be called on User interaction, otherwise, the LedgerDevice communication library will throw an exception.
const establishConnection = () => {
// Set the desired signingMechanism.
// await sologenic.setSigngMechanism(new ƨ.LedgerDeviceSigner({
// ripple_server: RIPPLE_SERVER // i.e.: wss://s1.ripple.com/
// }));
// await sologenic.setSigngMechanism(new ƨ.DcentSigner());
// await sologenic.setSigngMechanism(new ƨ.XummWalletSigner({
// server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/',
// container_id: 'qr_container',
// fallback_container_id: 'qr_container_fallback',
// }));
await sologenic.setSigningMechanism(new ƨ.SoloWalletSigner({
server: 'https://api.sologenic.org/api/v1/',
container_id: 'qr_container',
fallback_container_id: 'qr_container_fallback'
}));
// Events have their own types now.
sologenic.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL QUEUED: ', event);
});
sologenic.on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL DISPATCHED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL REQUEUED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL WARNING:', event);
});
sologenic.on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL VALIDATED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL FAILED:', event);
});
// Get Signing Mechanism and fetch for Wallet Address.
const { address } = await sologenic.connectSigner();
await sologenic.setAccount({
address: address
});
const tx = sologenic.submit({
TransactionType: 'Payment',
Account: address,
Destination: 'rUwty6Pf4gzUmCLVuKwrRWPYaUiUiku8Rg',
Amount: {
currency: '534F4C4F00000000000000000000000000000000',
issuer: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
value: '100000000'
}
});
// At this point, the SigningMechanism will trigger the Signing Request on the corresponding
// device. LedgerDevice, Dcent, SOLO Wallet or XUMM Wallet
// Events have their own types now.
tx.events.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX QUEUED: ', event);
}).on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('TX DISPATCHED:', event);
}).on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX REQUEUED:', event);
}).on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('TX WARNING:', event);
}).on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('TX VALIDATED:', event);
});.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('TX FAILED:', event);
});
console.log(await tx.promise);
})();'use strict';
const ƨ = require('sologenic-xrpl-stream-js');
(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: "hash",
hash: {}
}
).connect();
// Events have their own types now.
sologenic.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL QUEUED: ', event);
});
sologenic.on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL DISPATCHED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL REQUEUED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL WARNING:', event);
});
sologenic.on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL VALIDATED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL FAILED:', event);
});
await sologenic.setAccount({
address: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
secret: 'ssH5SSKYvHBynnrYoCnmvsbxrNGEv'
});
const tx = sologenic.submit({
TransactionType: 'Payment',
Account: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
Destination: 'rUwty6Pf4gzUmCLVuKwrRWPYaUiUiku8Rg',
Amount: {
currency: '534F4C4F00000000000000000000000000000000',
issuer: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
value: '100000000'
}
});
// Events have their own types now.
tx.events.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX QUEUED: ', event);
}).on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('TX DISPATCHED:', event);
}).on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX REQUEUED:', event);
}).on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('TX WARNING:', event);
}).on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('TX VALIDATED:', event);
});.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('TX FAILED:', event);
});
console.log(await tx.promise);
} catch (error) {
console.log('Error:', error);
}
})();(async () => {
try {
const sologenic = await new ƨ.SologenicTxHandler(
// RippleAPI Options
{
server: 'wss://testnet.xrpl-labs.com', // Kudos to Wietse Wind
},
// Sologenic Options, hash or redis
{
clearCache: true,
queueType: "hash",
hash: {}
}
).connect();
// Events have their own types now.
sologenic.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL QUEUED: ', event);
});
sologenic.on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL DISPATCHED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL REQUEUED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL WARNING:', event);
});
sologenic.on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL VALIDATED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL FAILED:', event);
});
await sologenic.setAccount({
address: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
keypair: {
publicKey: 'my public key with permission to sign transaction for address',
privateKey: 'my private key with permission to sign transactions for address'
}
});
const tx = sologenic.submit({
TransactionType: 'Payment',
Account: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
Destination: 'rUwty6Pf4gzUmCLVuKwrRWPYaUiUiku8Rg',
Amount: {
currency: '534F4C4F00000000000000000000000000000000',
issuer: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
value: '100000000'
}
});
// Events have their own types now.
tx.events.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX QUEUED: ', event);
}).on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('TX DISPATCHED:', event);
}).on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX REQUEUED:', event);
}).on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('TX WARNING:', event);
}).on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('TX VALIDATED:', event);
});.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('TX FAILED:', event);
});
console.log(await tx.promise);
} catch (error) {
console.log('Error:', error);
}
})();There are 6 different events that you'll receive while a transaction is being processed by the library. Each event has its own type associated with it as you can see in the src/types/sologenicoptions.d.ts. See below for a list of events and the emitted objects.
-
Event (validated):
SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent -
Event (warning):
SologenicTypes.WarningEvent -
Event (requeued):
SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent -
Event (queued):
SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent -
Event (failed):
SologenicTypes.FailedEvent -
Event (dispatched):
SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent
As you can see below in the transactions section there is a snippet of code there. The reason we added this is because we wanted to outline that we have two separate event emitters that emit events based on the transactions. One of the event emitters being a global emitter that receives all events, and then a transaction based event emitter which receives events for only the transaction it has subscribed to.
For example, the sologenic.on() subscriptions (event listeners) to events are global, meaning you'll receive events for every transaction you submit. Whereas, the tx.events.on() subscriptions (event listeners) are specific to the transactions themselves, once the transaction has been validated or failed you will no longer receive transactions as the listeners are all unsubscribed automatically.
// Events have their own types now.
sologenic.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL QUEUED: ', event);
});
sologenic.on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL DISPATCHED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL REQUEUED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL WARNING:', event);
});
sologenic.on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL VALIDATED:', event);
});
sologenic.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('GLOBAL FAILED:', event);
});
await sologenic.setAccount({
address: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
keypair: {
publicKey: 'my public key with permission to sign transaction for address',
privateKey: 'my private key with permission to sign transactions for address'
}
});
const tx = sologenic.submit({
TransactionType: 'Payment',
Account: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
Destination: 'rUwty6Pf4gzUmCLVuKwrRWPYaUiUiku8Rg',
Amount: {
currency: '534F4C4F00000000000000000000000000000000',
issuer: 'rNbe8nh1K6nDC5XNsdAzHMtgYDXHZB486G',
value: '100000000'
}
});
// Events have their own types now.
tx.events.on('queued', (event: SologenicTypes.QueuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX QUEUED: ', event);
}).on('dispatched', (event: SologenicTypes.DispatchedEvent) => {
console.log('TX DISPATCHED:', event);
}).on('requeued', (event: SologenicTypes.RequeuedEvent) => {
console.log('TX REQUEUED:', event);
}).on('warning', (event: SologenicTypes.WarningEvent) => {
console.log('TX WARNING:', event);
}).on('validated', (event: SologenicTypes.ValidatedEvent) => {
console.log('TX VALIDATED:', event);
});.on('failed', (event: SologenicTypes.FailedEvent) => {
console.log('TX FAILED:', event);
});Each transaction that is created by the sologenic-xrpl-stream-js library will have a unique uuidv4 that is used for tracking purposes in the queue system. The tx.id is not the same as the XRPL ledger hash.
Example snippet from src/lib/sologenictxhandler.ts
public submit(tx: SologenicTypes.TX): SologenicTypes.TransactionObject {
try {
// Generate a unique ID using the uuid library
const id = uuid();
// Add a new EventEmitter to txEvents array identifiable with the generated id.
this.txEvents![id] = new EventEmitter();
this._initiateTx(id, tx);When you are receiving events while the transaction is undergoing processing in the XRPL, you'll receive your transaction ID which can be then used to verify your transaction has been completed. In addition, once the transaction has been validated in the XRPL, you will notice that the tx.id is appended to a memo-field within the transaction itself.
The tx.id field is non-async and does not change if the transaction is requeued or failed so that you have the option of going back to check the state.