temporalstate 

Quick start
Temporal state is a library for building, manipulating and deriving the state of a collection of variables over time. It is efficient, using binary trees, and will scale to big data sets.
For example, if you create a temporalstate object and tell it the weather
is "raining" at t = 5 it can then be derived that the weather is
null from the start of time until t = 5, and from then until the end
of time it is "raining". You can derive the value for weather at any
time in fact.
If you also add that the moon is "crescent" at t = 3 and introduce
data concerning any number of other variables, then the full set of all variable
values can be derived for any given time.
The value of any variable before the time of its first value will be
null, and the chronologically last value of a variable will persist forever.
Take this example time line, with three variables, weather, moon and sun:
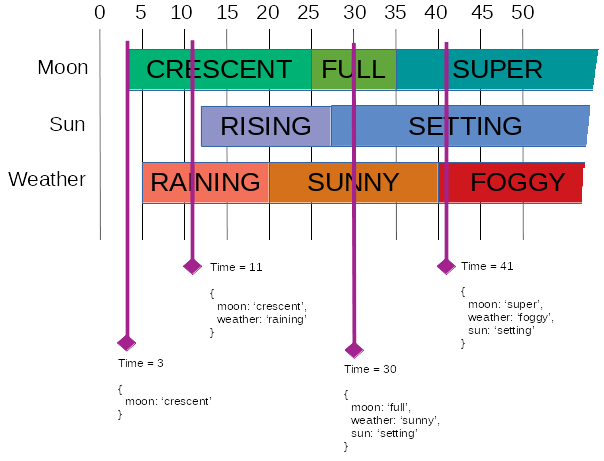
Building up this state would be done as follows:
; let db = ; db;db;db;db;db;db;db;db;It doesn't matter what order the state changes are added, the state of the whole thing will always reflect the changes that have been entered in so far.
The state of a single variable at any time can be queried by calling state()
with two arguments:
db == nulldb == nulldb == 'crescent'db == 'crescent'db == 'crescent'db == 'full'db == 'super'db == 'super'db == 'super'The state of all variables at any time can be queried by calling state()
with a single argument:
db == {}db == weather: 'raining' moon: 'crescent' db == weather: 'sunny' moon: 'crescent' sun: 'rising' db == weather: 'sunny' moon: 'full' sun: 'setting' db == weather: 'foggy' moon: 'super' sun: 'setting' db == weather: 'foggy' moon: 'super' sun: 'setting' You can also regurgitate all the changes which constitute the current
all time state by calling change_list():
db === timestamp: 3 name: 'moon' val: 'crescent' timestamp: 5 name: 'weather' val: 'raining' timestamp: 12 name: 'sun' val: 'rising' timestamp: 20 name: 'weather' val: 'sunny' timestamp: 25 name: 'moon' val: 'full' timestamp: 27 name: 'sun' val: 'setting' timestamp: 35 name: 'moon' val: 'super' timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' Note that this data is parsimonious, no valueless data is kept, so if you add a change to the effect that it is raining at time 5, this will not change the change list or any other derivation at all. Similarly if it is raining at 5, sunny at 10 and raining again at 15, if you then say it is raining at 10 the number of changes is optimised down to just the one rainining at 5 record.
The time is given as an integer in the examples above, but a Date object, a float or a string can be used instead. Anything that can be compared with the less than and greater than comparison operators will work.
Contents
- Quick start.
- Contents.
- Full API reference.
- Functions.
- constructor.
- add_change.
- remove_change.
- change_list.
- var_list.
- first.
- last.
- next.
- prev.
- at.
- after.
- before.
- state.
- state_detail.
- remove_var.
- change_cmp.
- Events.
- Functions.
Full API reference
Import the temporalstate constructor with import:
;Or with require:
let temporalstate = default;Functions
constructor
Constructs a temporalstate object.
let db = ;NOTE in the examples of this documentation, simple scalar values
are employed; strings such as 'raining' and 'super'. There is
nothing to stop you from using complex structures instead EXCEPT
that temporalstate needs to know how to determine their
equality! So, if you use complex structures you must provide
an equality checking function, like this:
let db = { // return true if the values are equal, otherwise false return JSON === JSON; };This one is a bit of a get out of jail free card because it is
highly likely to work for almost any structure you employ. Use
this if it is appropriate, but an equality function more
specific to your data might be more efficient (for example the
function function (a, b) { return a.complex === b.complex; }
is used in the unit tests), if that is possible.
add_change
Adds a change to the temporal data. If the change is redundant or renders other current changes redundant they will be trimmed so that the data is always kept parsimonious.
A single object parameter with 'timestamp', 'name' and 'val' keys is required, these being the time of the change, the name of the variable changing and the value it is changing to.
db;db;db;remove_change
Removes a change. The call will have no affect if the change does not exist.
db;change_list
Returns the set of all known changes.
let changes = db;Here, changes will be a list of objects, each with timestamp,
name and a val keys, for example like this:
timestamp: 3 name: 'moon' val: 'crescent' timestamp: 5 name: 'weather' val: 'raining' timestamp: 12 name: 'sun' val: 'rising' timestamp: 20 name: 'weather' val: 'sunny' timestamp: 25 name: 'moon' val: 'full' timestamp: 27 name: 'sun' val: 'setting' timestamp: 35 name: 'moon' val: 'super' timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' var_list
Returns a list of known variables. This will include variables without states, if there are any. The result is sorted.
let vars = db;Here, vars will be a list of variable names, like this:
'moon' 'sun' 'weather'first
Without a parameter, first() returns the first change(s) (i.e.
the first ranked by time). The return value is a list, and will
contain all the changes which have a time equal to the lowest time
in the database. So this will probably usually be a list of one
change, but could be any number. The return value can also be null
if there are no changes in the database.
let first_changes = db;Here, first_changes will be a list of objects just like those
returned by change_list above:
timestamp: 3 name: 'moon' val: 'crescent' Or it could be:
timestamp: 3 name: 'moon' val: 'crescent' timestamp: 3 name: 'temperature' val: 22 The time will always be the same if there are multiple changes.
If a variable name is passed as a parameter, only that variable is considered and a single change is returned instead of a list. For example:
let first_change = db;Here first_change could be:
{ timestamp: 3, name: 'moon', val: 'crescent' }
last
This is like first but it returns the last change(s).
Again there can be multiple changes if their time is the same
and again the return value can instead be null if there are
no changes in the database. Also if a parameter is employed
to provide a variable name, then a single change is returned
(the last of that variable).
let last_changes = db;Here, last_changes will be a list of objects just like those
returned by change_list and first
above:
timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' Or it could be:
timestamp: 40 name: 'temperature' val: 18 timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' If a variable name is passed as a parameter, only that variable is considered and a single change is returned instead of a list. For example:
let last_change = db;Here last_change could be:
{ timestamp: 40, name: 'weather', val: 'foggy' }
next
This returns the next change (after the one passed as an argument). If one paramter is given then much like first and last, multiple changes may be returned if they are of the same time.
let next_changes = dbnexttimestamp: 20 name: 'weather' val: 'sunny';Here, next_changes will be a list of objects, like:
timestamp: 25 name: 'moon' val: 'full' Or it could be:
timestamp: 25 name: 'moon' val: 'full' timestamp: 25 name: 'temperature' val: 25 If a second parameter is given, then either null or the next
change for that variable is returned (not an array of changes).
prev
This returns the previous change (after the one passed as an argument). If one paramter is given then much like prev multiple changes may be returned if they are of the same time.
let prev_changes = db;Here, prev_changes will be a list of objects, like:
timestamp: 12 name: 'sun' val: 'rising' Or it could be:
timestamp: 12 name: 'sun' val: 'rising' timestamp: 12 name: 'temperature' val: 14 If a second parameter is given, then either null or the previous
change for that variable is returned (not an array of changes).
at
Returns the change(s) occurring at exactly the specified time. The required time is passed as an argument. Because multiple changes (of different variables) could match the return value is an array. For example:
let changes_at = db;Returns an empty list if there are no changes at the specified time.
If a variable name is specified as an argument, then a single
change is returned, or null if there is none at the specified
time.
after
Returns the change(s) occurring closest after the specified time. The required time is passed as an argument. Because multiple changes (of different variables) could match (if they share the closest time) the return value is an array. For example:
let changes_after = db;If the time specified is after the last known change, then
null is returned.
before
Returns the change(s) occurring closest before the specified time. The required time is passed as an argument. Because multiple changes (of different variables) could match (if they share the closest time) the return value is an array. For example:
let changes_before = db;If the time specified is before the first known change, then
null is returned.
state
Returns the state at any given time. Takes either one or two arguments, the first, compulsory parameter, is the time, and the second is the name of a state. If no state name is given then all states that have a value at the given time will be returned as an object, with the keys being state names and the values being the state values. Where a state name is given the return value will be the states value, or null if it does not have a value at that time.
With a single argument:
all_states_at_20_time = db;Here all_states_at_20_time will contain something like this:
weather: 'sunny' moon: 'crescent' sun: 'rising' With a second argument:
weather_at_20_time = db;Here weather_at_20_time will contain something like this:
'sunny'state_detail
State detail, like state takes one or two arguments, the time, and optionally a state name. It also similarly returns state data, but instead of just the state values at the specified time it returns data concerning when the state became that value (which will be at or before the time passed as argument one) and data concerning when it ceases to be that value (which will be after the time passed as argument one) and what the next value is.
The return value when a second argument (state name) is passed
is of the form {'from': current_change, 'to': next_change}, where
current_change and next_change are formatted like the
changes returned by change_list, something like
{ timestamp: 3, name: 'moon', val: 'crescent' }.
let weather_details_at_20_time = db;The value of weather_details_at_20_time would now be something
like:
from: timestamp: 20 name: 'weather' val: 'sunny' to: timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' The return value when only a single argument (the time) is passed is a list of such from to structures.
In all cases, where the time given is before the first value of a
state, null is the to value, and where the time given is after
the last change (or equal in time to it), null is the from
value. Where no data exists for a state name the return value or
the state name is unknown, then null is returned instead of
{'from': null, 'to': null}, for that state.
let all_states_at_30_time = db;The value of all_states_at_30_time would now be something
like:
from: timestamp: 25 name: 'moon' val: 'full' to: timestamp: 35 name: 'moon' val: 'super' from: timestamp: 27 name: 'sun' val: 'setting' to: null from: timestamp: 20 name: 'weather' val: 'sunny' to: timestamp: 40 name: 'weather' val: 'foggy' The ordering of the list is done by the state name
remove_var
When removing a change (explicitly or implicitly), if it is the last
remaining change in the database, though there will be no changes
for that variable any more, the variable will still exist; calling
var_list() will list it.
If it is desirable to get rid of it entirely, call remove_var
and provide the variable name as a parameter. For example:
db;If a variable is removed true is returned, or else false.
A variable is not removed if it does not exist, or if it has changes (i.e. it must be unused).
change_cmp
This is a static function, not a class method, it takes two arguments and provides the sort order for changes (as returned by change_list) by returning 1, 0 or -1, like all sort element comparison functions.
The order of changes is determined first by the time of the change, and then by the name of the state.
Events
Events are emitted before a change actually takes effect. In the case of transaction events, the txn_start, is emitted first of all, then applicable add and rm events one by one proceeded by the execution of the respective add or remove action, and finally the txn_end event.
new_var
The new_var event is emitted when a new variable is realised. Adding an event with a variable name not seen before will cause this.
db;rm_var
The rm_var event is emitted when a new variable is removed.
This can only happen as a result of a call to remove_var.
db;add
The add event is emitted when a change is added to the database.
db;Note that this event will only fire for an actual change, so if a change is added that is redundant, no event will occur.
rm
The rm event is emitted when a change is eliminated from the database.
db;Changes may be removed to preserve the parsimony of the database so the change removal need not be explicit.
change
The change event is emitted when a change is made that alters the value of an existing variable at a time when that variable already has a change.
db;txn_start
The txn_start event is emitted when any change occurs. A change may result in multiple operations however (and hence as a result a number of add, rm or change events may be emitted) so if it is desired to either capture these as one transaction or to capture the original requested change that caused them, the transaction events should be used (txn_start or txn_end).
db;For example, if the following changes are added (to an empty database):
db;db;db;Then this change is added:
db;The txn_start event will be emitted with the first argument being
{'add': {'timestamp': 20, 'name': 'weather', 'val': 'raining'}}
and the second being [{'remove': {'timestamp': 20, 'name': 'weather', 'val': 'sunny'}}, {'remove': {'timestamp': 30, 'name': 'weather', 'val': 'raining'}}].
Most changes will of course usually result in a transaction with a single operation which is identical to the actual change requested.
If a change is due to a remove_change call instead of a add_change
then there can only be one operation, but in addition to the rm
event, a txn_start even is also emitted. In the case of the following
removal for example:
db;...the txn_start event will be emitted with the first argument being
{'remove': {'timestamp': 20, 'name': 'weather', 'val': 'raining'}}
and the second being [{'remove': {'timestamp': 20, 'name': 'weather', 'val': 'raining'}}].
txn_end
The txn_end event is exactly like the txn_start event described above, except that it is emitted after all the changes have been executed.