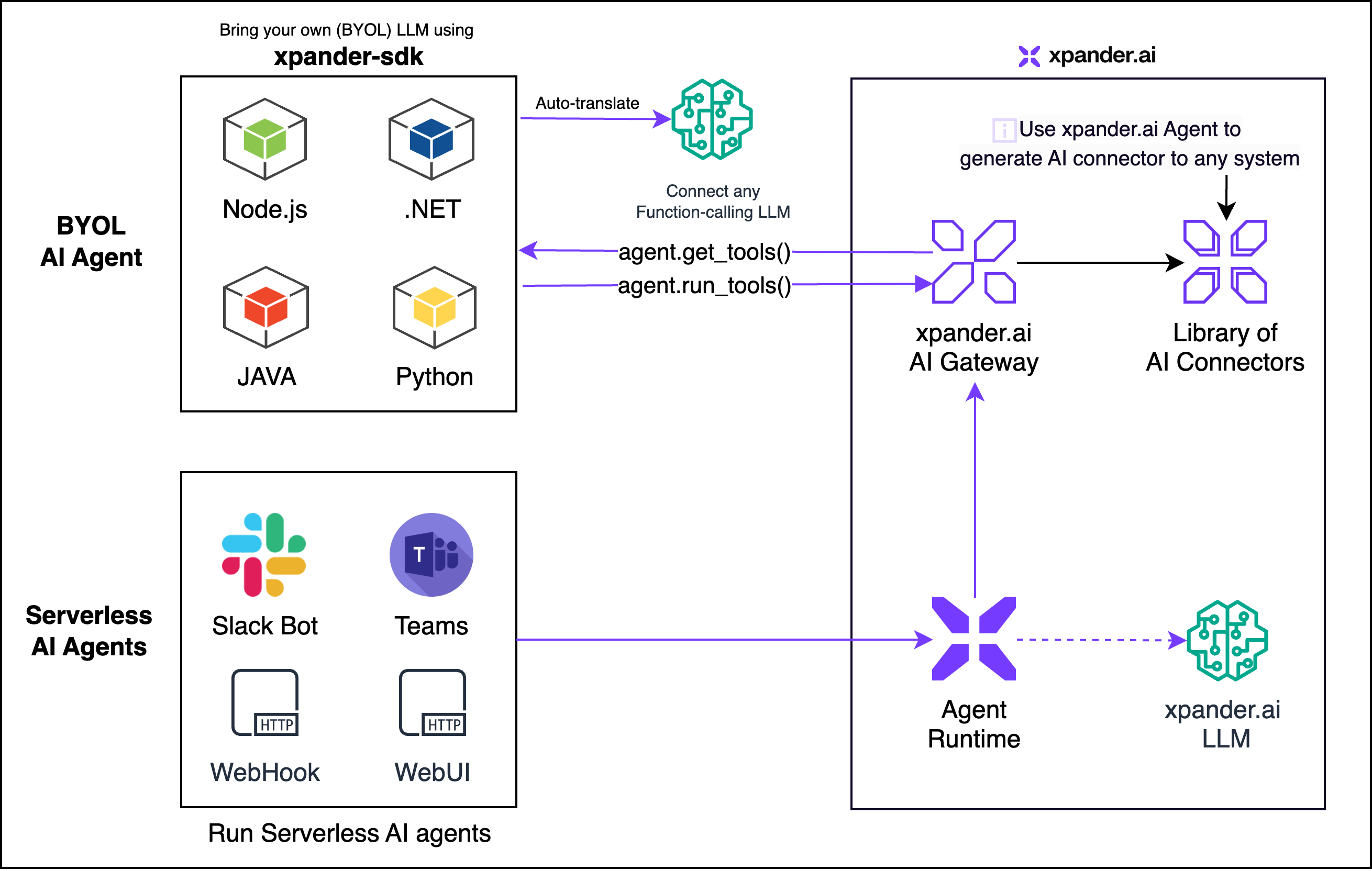
Xpander Open Source SDK empowers developers to build intelligent and reliable AI Agents capable of managing complex, multi‑step tasks across diverse systems and platforms. The SDK simplifies challenges like function calling, schema definition, graph enforcement, and prompt group management.
With first‑class support for leading LLM providers such as OpenAI, Amazon Bedrock, Google Gemini, Anthropic Claude, and NVIDIA NIM, the Xpander SDK seamlessly integrates into your existing systems.
Choose your preferred package manager:
npm install xpander-sdkpip install xpander-sdk- Sign in to app.xpander.ai and create (or pick) an Agent.
- Copy the Agent Key and Agent ID from the Agent → Settings page.
- Grab the API key for your preferred LLM provider (e.g.
OPENAI_API_KEY,GEMINI_API_KEY, etc.). - Install the SDK (see above) and make sure you have Node.js installed – the SDK runs a tiny Node.js runtime under the hood.
Below are the canonical patterns taken from the official documentation for working with LLMs through the Xpander SDK.
from xpander_sdk import XpanderClient, LLMProvider
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
xpander_client = XpanderClient(api_key=os.getenv("XPANDER_API_KEY"))
agent = xpander_client.agents.get(agent_id=os.getenv("XPANDER_AGENT_ID"))
openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
# A one‑off prompt handled by the agent + tools
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=agent.messages, # current conversation state
tools=agent.get_tools(llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI),
tool_choice="auto",
temperature=0.0,
)
# Let the SDK execute the tool calls & keep state in sync
agent.process_llm_response(response.model_dump(), llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI)Tip:
agent.process_llm_response(...)is the easiest way to both store the assistant message and immediately run any tool calls it contains – perfect for serverless single‑turn workflows.
from xpander_utils.events import (
XpanderEventListener,
AgentExecutionResult,
ExecutionStatus,
AgentExecution,
)
from xpander_sdk import XpanderClient, LLMProvider
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
listener = XpanderEventListener(
api_key=os.getenv("XPANDER_API_KEY"),
organization_id=os.getenv("XPANDER_ORG_ID"),
agent_id=os.getenv("XPANDER_AGENT_ID"),
)
# Optional helper clients (LLM + Agent)
openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
xpander_client = XpanderClient(api_key=os.getenv("XPANDER_API_KEY"))
agent = xpander_client.agents.get(agent_id=os.getenv("XPANDER_AGENT_ID"))
def on_execution_request(execution_task: AgentExecution) -> AgentExecutionResult:
"""Runs each time your cloud Agent triggers an execution request."""
# (1) Ask the LLM what to do next
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=agent.messages,
tools=agent.get_tools(llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI),
tool_choice="auto",
temperature=0.0,
)
# (2) Persist the assistant message *and* execute any tool calls
agent.process_llm_response(response.model_dump(), llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI)
# (3) Return the final result back to the platform
return AgentExecutionResult(
result=execution_status.result,
is_success=True if execution_status.status == ExecutionStatus.COMPLETED else False,
)
# Block forever, listening for events via SSE
listener.register(on_execution_request=on_execution_request)Why
xpander-utils? TheXpanderEventListeneruses a lightweight Server‑Sent Events (SSE) channel to deliver execution requests to your code with sub‑second latency—perfect for Slack, Teams, and other real‑time chat surfaces. (pypi.org)
# Describe a complex objective for the agent
multi_step_task = """
Find employees of xpander.ai and their roles.
Then check their LinkedIn profiles for recent updates.
"""
agent.add_task(multi_step_task) # automatically initialises memory
while not agent.is_finished():
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=agent.messages,
tools=agent.get_tools(llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI),
tool_choice="auto",
temperature=0.0,
)
agent.process_llm_response(response.model_dump(), llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI)
# 🚀 Grab the final result once the agent marks itself as finished
execution_result = agent.retrieve_execution_result()
print(execution_result.status) # e.g. "SUCCEEDED"
print(execution_result.result) # your task outputThis loop lets the LLM break the objective into sub‑steps, call tools, update memory and eventually mark the task as finished.
from xpander_sdk import XpanderClient, LLMProvider
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from os import environ
load_dotenv()
xpander_client = XpanderClient(api_key=environ["XPANDER_API_KEY"])
gemini_client = OpenAI(
api_key=environ["GEMINI_API_KEY"],
base_url="https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/openai/",
)
agent = xpander_client.agents.get(agent_id=environ["XPANDER_AGENT_ID"])
agent.add_task("Find employees of xpander.ai.")
while not agent.is_finished():
response = gemini_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
messages=agent.messages,
tools=agent.get_tools(llm_provider=LLMProvider.GEMINI_OPEN_AI),
tool_choice=agent.tool_choice,
temperature=0.0,
)
agent.add_messages(response.model_dump())
tool_calls = XpanderClient.extract_tool_calls(
llm_response=response.model_dump(),
llm_provider=LLMProvider.GEMINI_OPEN_AI,
)
agent.run_tools(tool_calls)
print(agent.retrieve_execution_result().result)This demo showcases full multi‑step orchestration without writing any provider‑specific glue code.
Local tools let you register your own functions (Python, TS, C#, …) so the LLM can request them. Important: the SDK does not execute local tools for you. Your code must:
- Register the tool schema with
agent.add_local_tools(). - Inspect each LLM response with
XpanderClient.extract_tool_calls(...). - Pick out the pending local calls via
retrieve_pending_local_tool_calls(...). - Invoke the matching Python/TS function(s).
- Feed a
ToolCallResultback withagent.memory.add_tool_call_results([...]).
from xpander_sdk import XpanderClient, LLMProvider, ToolCallResult
from openai import OpenAI
from local_tools import local_tools_declarations, local_tools_by_name
client = XpanderClient(api_key=XPANDER_API_KEY)
agent = client.agents.get(agent_id=XPANDER_AGENT_ID)
openai = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
# 1️⃣ Tell the agent about your local tools
agent.add_local_tools(local_tools_declarations)
# 2️⃣ Normal chat ‑ the LLM may now reference those tools
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=agent.messages,
tools=agent.get_tools(llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI),
tool_choice="auto",
temperature=0.0,
)
# 3️⃣ Extract *all* tool calls & isolate locals
all_calls = XpanderClient.extract_tool_calls(response.model_dump(), llm_provider=LLMProvider.OPEN_AI)
pending_local = XpanderClient.retrieve_pending_local_tool_calls(all_calls)
# 4️⃣ Run each local call
results = []
for call in pending_local:
fn = local_tools_by_name[call.name]
output_payload = fn(**call.payload) # your function runs here
results.append(
ToolCallResult(
function_name=call.name,
tool_call_id=call.tool_call_id,
payload=call.payload,
status_code=200,
result=output_payload,
is_success=True,
is_retryable=False,
)
)
# 5️⃣ Write the results back so the LLM can continue
agent.memory.add_tool_call_results(results)// localTools array holds { decleration, fn }
agent.addLocalTools(localToolsDecleration);
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: 'gpt-4o',
messages: agent.messages,
tools: agent.getTools(),
tool_choice: agent.toolChoice,
});
const toolCalls = XpanderClient.extractToolCalls(response);
const pendingLocalCalls = XpanderClient.retrievePendingLocalToolCalls(toolCalls);
for (const call of pendingLocalCalls) {
const resultPayload = localToolsByName[call.name](...Object.values(call.payload));
agent.memory.addToolCallResults([
new ToolCallResult(
call.name,
call.toolCallId,
call.payload,
200,
resultPayload,
true,
false,
),
]);
}The LLM will then see the tool responses in its context and proceed to the next reasoning step. This mirrors the official test‑suite workflow.
-
Create a task first –
agent.add_task()automatically initialises the agent’s memory and system messages. -
Always pass
llm_providerwhen callingagent.get_tools()so the SDK can return the correct schema for the target provider. -
Store the raw LLM response with
agent.add_messages(...)(or implicitly viaagent.process_llm_response). The SDK will convert fields as required. -
Extract tool calls with the same provider flag you used for
get_tools:XpanderClient.extract_tool_calls(llm_response, llm_provider=...).
Following these rules ensures your code works consistently across OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Bedrock, and more.
- Official Documentation: https://docs.xpander.ai/userguides/overview/introduction
- LLM SDK Guide: https://docs.xpander.ai/docs/01-get-started/03-llm-models
- API Reference: https://docs.xpander.ai/api-reference/SDK/getting-started
The library is generated with Projen and runs inside a tiny Node.js runtime. Ensure you have a recent Node.js version installed for optimal performance.
We welcome contributions to improve the SDK. Please see our CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines on how to submit improvements and bug fixes.