
XSM - State Management made eXtraordinarily simple and effective for Angular, React, Vue, and Svelte.
🏠 Homepage
Demos
Realworld Example App with react-xsm
Highlights
- Incredibly easy to use, developer friendly and minimum learning curve
- Reactive, unintrusive
- Automatic re-rendering and state data removal, efficient memory management
- Super simple async handling
- Same API for Angular, React, Vue, and Svelte, code reuse, framework agnostic
- Small size for fast download, no framework specific plugins needed.
| Library | Minzipped Size |
|---|---|
| XSM |
|
| Redux |
|
| react-Redux |
|
| mobx |
|
| mobx-react |
|
| Vuex |
|
| RXJS |
|
Benchmark Results
XSM is performant according to Stefan Krause's js-framework-benchmark. As shown below,
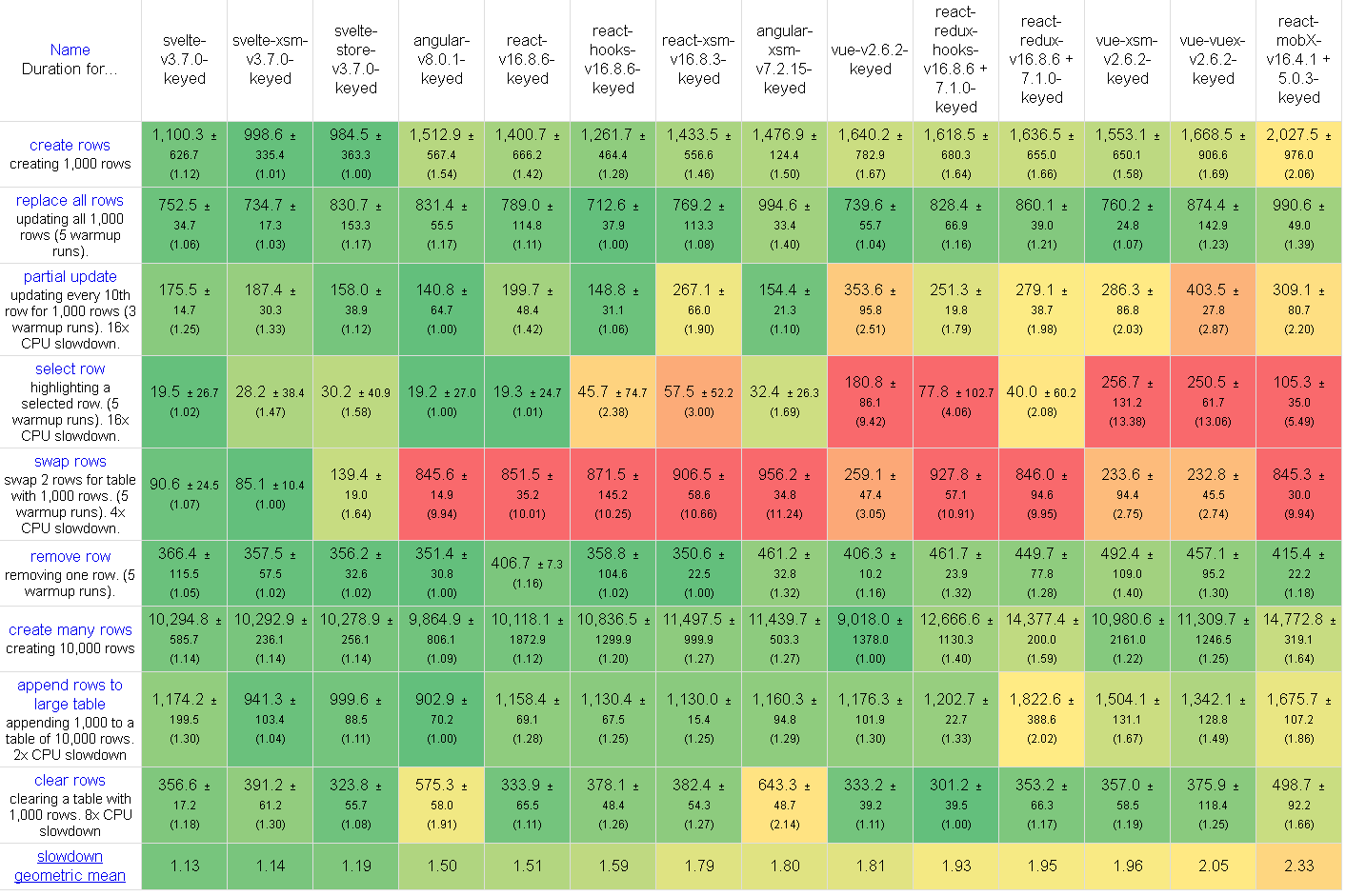 .
.
The code for the benchmarks is in this repo.
How-to's
Install
npm install xsmUsage in Brief
- Tell XSM which framework to use
- Bind the component state to XSM
- When you are ready to update the state(sync or async)
Component will be re-rendered automatically.
Debug and Trace
Both debug and trace can be selectively turn on and off at any point
//debug on //debug off //trace on //trace offWhy XSM
To answer why, let's start by answering another question, what is XSM? It consists of a global store and the machinary to re-render the component when the state is updated. The store is just a javascript object with key and value pairs. By binding the instance reference, this, to the store, each component can react to the changes of the store whether it is re-render or unmount. It is really this simple, no need to use HOC, provider, reducer, decorator, observer, action, dispatcher, etc. Hence, all the three most popular frameworks work the same way in XSM and that's why we can keep the code size very small and support the three frameworks without framework specific modules. Svelte is very different from other frameworks. It is this less. The state object becomes this.
API
bindState - binds a component's this and optionally state to the store. The state is an object with key and value pairs. For Svelte, the value is a fuction that wraps the assignment of the value.
//Angular, React, Vue //Svelte is this less, state is {key: val => stateVariable = val}unbindState - If a component is mounted and unmounted repeatedly, you need to unbind the component state from the store when the component unmounts to prevent memory leak. This is needed for Svelte only. The unbinding is done aotumatically with the other frameworks by XSM.
//Svelte onlyget - gets the value of a given key from the store.
set - updates the store with the value for a given key and re-renders the component(s).
setMany - updates the store for the given key and value pairs and re-renders the component(s).
setup - It takes an object as an argument and is used for telling XSM which framework you app uses and optionally for binding the state of all components of the app to the store as well as turning the debug and trace on and off.
- frameworkValue: Angular, React, Vue, or Svelte
- ComponentName: It is the class name for React and Angular. It is the registered component name for Vue. Does not apply to Svelte.
- bindings: It serves two purposes. One is to bind the state of each component to the store and you don't need to binState in this case. Another is to tell XSM that which piece of data is shared by more than one components and the shared data will not be deleted even if the the components are unmounted. Does not apply to Svelte.
setcfg - It is an alias of setup.
User Guide
To use XSM to manage you app state, here are the steps to follow:
-
Use setup to bind XSM to a framework. Currently, XSM supports Angular, Reatc, Vue, and Svelte.
-
Bind the component state to the store with bindState to enble the auto re-rendering when the state is updated. The value of each bound key can be accessed in the component with this.keyname. For example, you want to bind a key and value pair of {title: 'XSM'} to a component,
-
For Angular and React, it is done in the constructor.
{super} -
For Vue, it can be done in the created life cycle hook.
{} -
For Svelte, it can be done inside the script tag of a component.
let title;let bindings = title = val;;//if needed; -
When it's time to update the state, use set when and where your state data is available whether it's in the await function, promise.then callback, plain old callback, or anywhere in your code path. XSM does not get in the way.
-
Besides the demos, you can find more code examples in this repository. A realworld example(implementing the Realworld Example Specs using XSM with React is in this repo. Angular and Vue verions will be implemented soon.
Author
👤 Peter Lu
- Github: @peterluhub
Show your support
Give a ⭐️ if this project helped you !
📝 License
This project is MIT licensed.
This README was originally generated with readme-md-generator

