ESLint Rule Benchmark times individual ESLint rules, capturing ops/sec, mean and median runtimes and rich latency percentiles to surface performance hotspots.
It helps you catch regressions and quantify optimization gains.
- Prevent performance regressions – catch slow rules before they reach production
- Compare implementations – find the fastest approach with side-by-side benchmarks
- Expose detailed metrics – ops/sec, mean, median, percentiles and more
- Track performance trends – export JSON results for historical analysis
- Benchmark real code – measure against actual projects, not synthetic snippets
-
Use TypeScript natively – run
.tsrules out of the box - Automate CI/CD checks – post performance impact straight to pull requests
- Generate multiple report formats – output to console, JSON or Markdown
- Install package:
npm install --save-dev eslint-rule-benchmark- Create a simple benchmark config
benchmark/config.jsorbenchmark/config.ts:
import { defineConfig } from 'eslint-rule-benchmark'
export default defineConfig({
tests: [
{
name: 'My Rule Performance',
ruleId: 'my-plugin/my-rule',
rulePath: '../rules/my-rule.js',
cases: [
{
testPath: './my-rule/base-case.js',
},
],
},
],
})- Run benchmarks:
npx eslint-rule-benchmark runBy default, eslint-rule-benchmark run will look for the config.{js,cjs,mts,ts,cts,mts} configuration file in the ./benchmark/ directory.
The configuration file should export a configuration object, preferably using the defineConfig helper for type safety and autocompletion.
import { defineConfig } from 'eslint-rule-benchmark'
export default defineConfig({
/* Number of measurement iterations. Default: 1000. */
iterations: 1000,
/* Warmup configuration. */
warmup: {
/* Number of warmup iterations. Default: 100. */
iterations: 100,
/* Whether to enable warmup. Default: true. */
enabled: true,
},
/* Max time per benchmark. Default: 5000. */
timeout: 5000,
/* Array of benchmark test specifications. */
tests: [
{
/* Descriptive name for this test group/specification. */
name: 'Rule: sort-imports',
/* ESLint rule identifier. */
ruleId: 'sort-imports',
/* Path to the rule's implementation. */
rulePath: '../lib/rules/sort-imports.ts',
/* Override global benchmark settings for this specific test group. */
iterations: 50,
timeout: 300,
warmup: {
iterations: 10,
},
/* Array of test cases for this rule. */
cases: [
{
testPath: './sort-imports/base-case.ts',
/* ESLint rule options specific to this case. */
options: [{ order: 'asc', ignoreCase: true }],
/* ESLint rule severity for this case (0, 1, 2). Default: 2. */
severity: 2,
},
{
testPath: './sort-imports/complex-case.ts',
},
],
},
{
name: 'Rule: sort-vars',
ruleId: 'sort-vars',
rulePath: '../lib/rules/sort-vars.ts',
cases: [
{
testPath: './sort-vars/base-case.ts',
},
],
},
/* ... more test specifications */
],
})ESLint Rule Benchmark provides the following performance metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Operations per second | Number of operations per second |
| Average time | Average execution time of the rule (e.g., in ms) |
| Median time (P50) | Median execution time (50th percentile) |
| Minimum time | Minimum execution time |
| Maximum time | Maximum execution time |
| Standard deviation | Standard deviation (measure of time variability) |
Metrics are available in Console, JSON, and Markdown formats, allowing integration with various systems and workflows.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rule: sort-imports
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sample | Ops/sec | Avg Time | Median | Min | Max | StdDev | Samples
base-alphabetical.ts | 7,569 ops/sec | 0.132 ms | 0.131 ms | 0.125 ms | 0.148 ms | ±0.004 ms | 7,421
base-natural.ts | 7,485 ops/sec | 0.134 ms | 0.132 ms | 0.126 ms | 0.151 ms | ±0.005 ms | 7,010
base-line-length.ts | 7,508 ops/sec | 0.133 ms | 0.131 ms | 0.125 ms | 0.150 ms | ±0.005 ms | 7,828
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
System Information:
Runtime: Node.js v22.15.1, V8 12.4.254.21-node.24, ESLint 9.25.1
Platform: darwin arm64 (24.5.0)
Hardware: Apple M1 Pro (10 cores, 2400 MHz), 32 GB RAM
ESLint Rule Benchmark automatically publishes benchmark results as comments to GitHub Pull Requests when running in GitHub Actions environment.
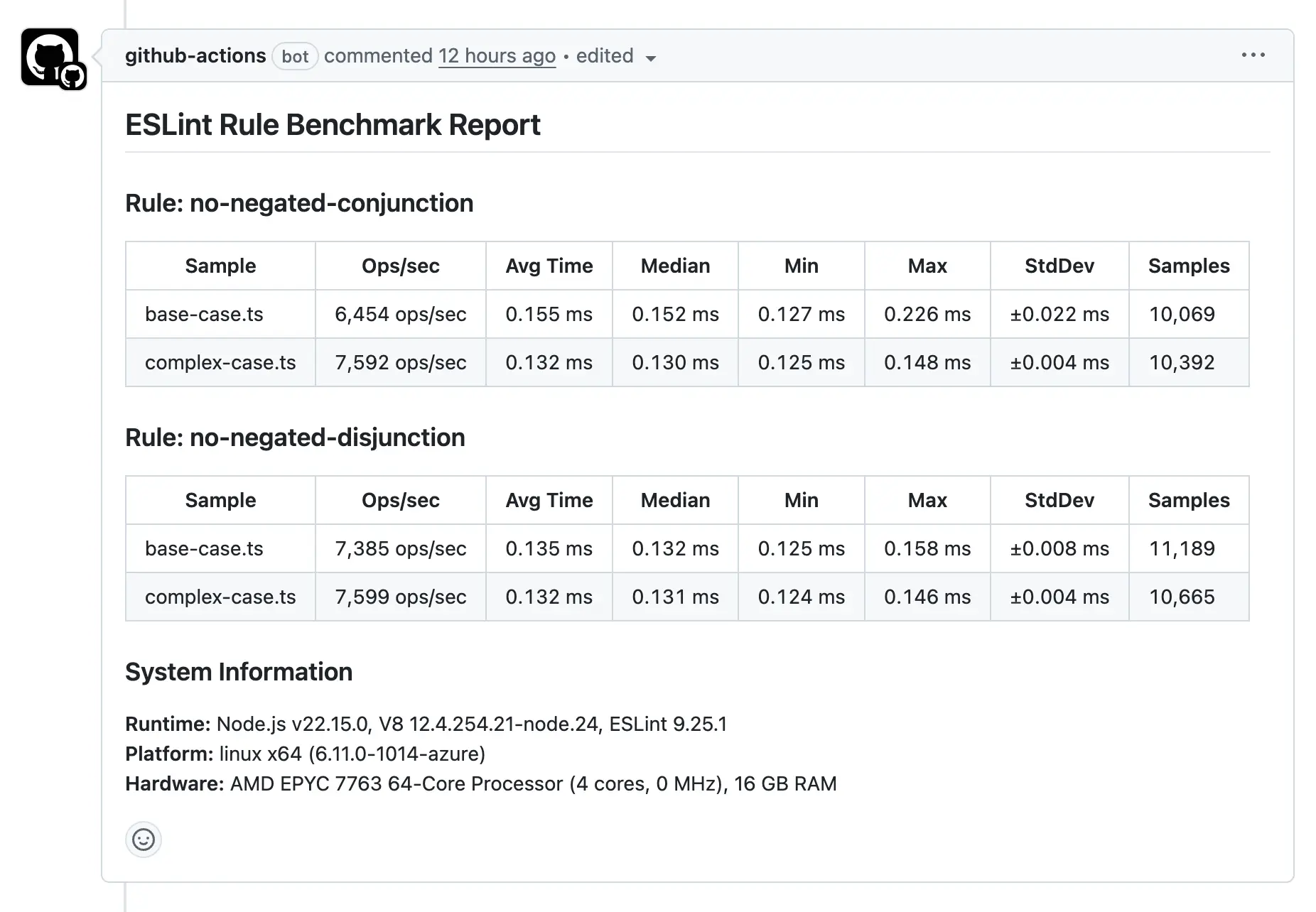
ESLint Rule Benchmark automatically posts benchmark results as comments on pull requests.
Create .github/workflows/benchmark.yml:
name: ESLint Rule Benchmark
on:
pull_request:
types: [opened, synchronize]
jobs:
benchmark:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
pull-requests: write
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '20'
- run: npm ci
- name: Run benchmark
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: npx eslint-rule-benchmark runThe tool uses Tinybench with warmup phases and outlier filtering for high accuracy.
The tool uses Tinybench for accurate and reliable benchmarking:
- Warmup phase to minimize JIT compilation impact
- Multiple iterations for statistical significance
- Isolation of the tested rule from other rules
- Outlier filtering (Tukey's fences method) for more stable and representative results, especially for maximum execution times.
Yes! Native TypeScript support is included.
This plugin is following Semantic Versioning.
See Contributing Guide.
MIT © Azat S.



