loopback-passport
The module provides integration between LoopBack and Passport to support third party login and account linking for LoopBack applications.
Use cases
Third party login
Social login becomes popular these days as our users don’t want to deal with so many identities. It would be nice to allow the use of a third party provider such as Facebook, Google, Twitter, or Github to log into LoopBack. The login profiles will be tracked and associated with corresponding LoopBack users.
Linked accounts
In LoopBack, most APIs will be built using models that are backed by data sources, which in turn uses connectors to interact with other systems or cloud services. Some of the backend systems require user-specific credentials to access the protected resources. For example, an e-commerce engine requires the user credential to see the order history. It’s also true to get pictures from one or more facebook accounts. One solution to this requirement is to link or pre-authorize a LoopBack user to other accounts.
Key components
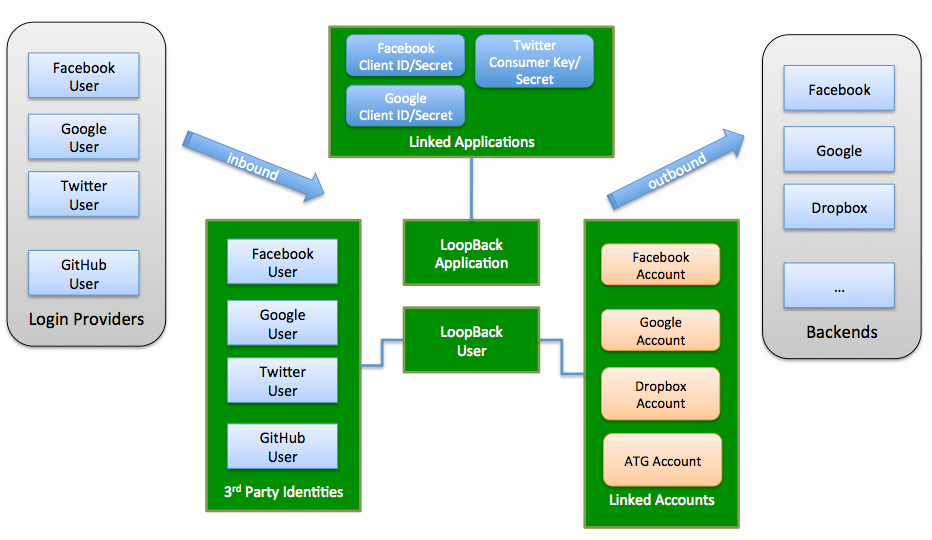
UserIdentity model
UserIdentity model keeps track of 3rd party login profiles. Each user identity is uniquely identified by provider and externalId. UserIdentity model comes with a 'belongsTo' relation to the User model.
Properties
- {String} provider: The auth provider name, such as facebook, google, twitter, linkedin
- {String} authScheme: The auth scheme, such as oAuth, oAuth 2.0, OpenID, OpenID Connect
- {String} externalId: The provider specific user id
- {Object} profile: The user profile, see http://passportjs.org/guide/profile
- {Object} credentials
- oAuth: token, tokenSecret
- oAuth 2.0: accessToken, refreshToken
- OpenID: openId
- OpenID Connect: accessToken, refreshToken, profile
- {*} userId: The LoopBack user id
- {Date} created: The created date
- {Date} modified: The last modified date
UserCredential model
UserCredential has the same set of properties as UserIdentity. It's used to store the credentials from a third party authentication/authorization provider to represent the permissions/authorizations from a user from the third party system.
ApplicationCredential model
Interacting with third party systems often require some client application level credentials. For example, you will need oAuth 2.0 client id and client secret to call facebook APIs. Such credentials can be supplied from a configuration file to your server globally. But if your server accepts API requests from multiple client applications, each client application should have its own credentials. To support the multi tenancy, this module provides the ApplicationCredential model to store credentials associated with a client application.
Properties
- {String} provider: The auth provider name, such as facebook, google, twitter, linkedin
- {String} authScheme: The auth scheme, such as oAuth, oAuth 2.0, OpenID, OpenID Connect
- {Object} credentials: The provider specific credentials
- openId: {returnURL: String, realm: String}
- oAuth2: {clientID: String, clientSecret: String, callbackURL: String}
- oAuth: {consumerKey: String, consumerSecret: String, callbackURL: String}
- {Date} created: The created date
- {Date} modified: The last modified date
ApplicationCredential model comes with a 'belongsTo' relation to the Application model.
PassportConfigurator
PassportConfigurator is the bridge between LoopBack and Passport.
- set up models with LoopBack
- initialize passport
- create Passport strategies from provider configurations
- set up routes for auth and callback
Flows
Third party login flow
The following steps use Facebook oAuth 2.0 login as an example.
- A visitor requests to log in using Facebook (or other providers), typically by clicking on a link or button backed by LoopBack to kick off oAuth 2.0 authorization code flow
- LoopBack redirects the browser to Facebook's authorization endpoint so that the user can log into Facebook and grant permissions to LoopBack
- Facebook redirects the browser to a callback URL hosted by LoopBack with the oAuth 2.0 authorization code
- LoopBack makes a request to the Facebook token endpoint to get an access token using the authorization code
- LoopBack uses the access token to retrieve the user's Facebook profile
- LoopBack searches the UserIdentity model by (provider, externalId) to see there is an existing LoopBack user for the given Facebook id
- If yes, set the LoopBack user to the current context
- If not, create a LoopBack user from the profile and create a corresponding record in UserIdentity to track the 3rd party login. Set the newly created user to the current context.
Third party account linking flow
The following steps use Facebook oAuth 2.0 login as an example.
- The user log into LoopBack first directly or through third party login
- The user clicks on a link or button by LoopBack to kick off oAuth 2.0 authorization code flow so that the user can grant permissions to LoopBack
- Perform the same steps 2-5 as third party login
- LoopBack searches the UserCredential model by (provider, externalId) to see there is an existing LoopBack user for the given Facebook id
- Link the Facebook account to the current user by creating a record in the UserCredential model to store the Facebook credentials, such as access token
- Now the LoopBack user wants to get a list of pictures from the linked Facebook account(s). LoopBack can look up the Facebook credentials associated with the current user and use them to call Facebook APIs to retrieve the pictures.
Use the module with a LoopBack application
A demo application is built with this module to showcase how to use the APIs with a LoopBack application. The code is available at:
https://github.com/strongloop-community/loopback-example-passport
Configure third party providers
The following example shows two providers: facebook-login for login with facebook and google-link for linking your google accounts with the current LoopBack user.
NOTE
You'll need to register with facebook and google to get your own client id and client secret.
- Facebook: https://developers.facebook.com/apps
- Google: https://console.developers.google.com/project
Add code snippets to app.js
var loopback = ;var path = ;var app = moduleexports = ; // Create an instance of PassportConfigurator with the app instancevar PassportConfigurator = PassportConfigurator;var passportConfigurator = app; app; ... // Enable http sessionapp; // Load the provider configurationsvar config = {};try config = ; catcherr console; console; process; // Initialize passportpassportConfigurator; // Set up related modelspassportConfigurator; // Configure passport strategies for third party auth providersforvar s in config var c = configs; csession = csession !== false; passportConfigurator;